Ionic Liquid Coating-Driven Nanoparticle Delivery to the Brain: Applications for NeuroHIV
- PMID: 38572510
- PMCID: PMC11186118
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202305484
Ionic Liquid Coating-Driven Nanoparticle Delivery to the Brain: Applications for NeuroHIV
Abstract
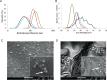
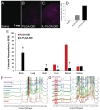
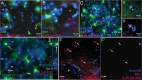
Delivering cargo to the central nervous system (CNS) remains a pharmacological challenge. For infectious diseases such as HIV, the CNS acts as a latent reservoir that is inadequately managed by systemic antiretrovirals (ARTs). ARTs thus cannot eradicate HIV, and given CNS infection, patients experience neurological deficits collectively referred to as "neuroHIV". Herein, the development of bioinspired ionic liquid-coated nanoparticles (IL-NPs) for in situ hitchhiking on red blood cells (RBCs) is reported, which enables 48% brain delivery of intracarotid arterial- infused cargo. Moreover, IL choline trans-2-hexenoate (CA2HA 1:2) demonstrates preferential accumulation in parenchymal microglia over endothelial cells post-delivery. This study further demonstrates successful loading of abacavir (ABC), an ART that is challenging to encapsulate, into IL-NPs, and verifies retention of antiviral efficacy in vitro. IL-NPs are not cytotoxic to primary human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and the CA2HA 1:2 coating itself confers notable anti-viremic capacity. In addition, in vitro cell culture assays show markedly increased uptake of IL-NPs into neural cells compared to bare PLGA nanoparticles. This work debuts bioinspired ionic liquids as promising nanoparticle coatings to assist CNS biodistribution and has the potential to revolutionize the delivery of cargos (i.e., drugs, viral vectors) through compartmental barriers such as the blood-brain-barrier (BBB).
Keywords: brain delivery; cellular hitchhiking; ionic liquids; nanoparticles; red blood cells.
© 2024 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
J.J.P. acknowledges a business relationship with Nephropathology Associates, PLC dba Arkana Laboratories. Business partners and funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results. E.E.L.T., C.M.H., and J.J.P. are named as inventors on provisional patents disclosing the results described here.
Figures


Update of
-
Ionic Liquid Coating-Driven Nanoparticle Delivery to the Brain: Applications for NeuroHIV.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 14:rs.3.rs-2574352. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2574352/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Jun;11(23):e2305484. doi: 10.1002/advs.202305484. PMID: 36824802 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Ionic Liquid Coating-Driven Nanoparticle Delivery to the Brain: Applications for NeuroHIV.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 14:rs.3.rs-2574352. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2574352/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Jun;11(23):e2305484. doi: 10.1002/advs.202305484. PMID: 36824802 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
An Elvitegravir Nanoformulation Crosses the Blood-Brain Barrier and Suppresses HIV-1 Replication in Microglia.Viruses. 2020 May 20;12(5):564. doi: 10.3390/v12050564. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32443728 Free PMC article.
-
Using microfluidic platforms to develop CNS-targeted polymeric nanoparticles for HIV therapy.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2019 May;138:111-124. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.01.014. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2019. PMID: 29397261
-
Development of ionic liquid-coated PLGA nanoparticles for applications in intravenous drug delivery.Nat Protoc. 2023 Aug;18(8):2509-2557. doi: 10.1038/s41596-023-00843-6. Epub 2023 Jul 19. Nat Protoc. 2023. PMID: 37468651 Review.
-
Approaches for CNS delivery of drugs - nose to brain targeting of antiretroviral agents as a potential attempt for complete elimination of major reservoir site of HIV to aid AIDS treatment.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2019 Mar;16(3):287-300. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2019.1583206. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2019. PMID: 30779602 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into the physicochemical interactions of ionic liquid-coated polymeric nanoparticles with red blood cells.Nanoscale Adv. 2025 Jul 11;7(17):5273-5283. doi: 10.1039/d5na00233h. eCollection 2025 Aug 19. Nanoscale Adv. 2025. PMID: 40704282 Free PMC article.
-
In situ cellular hitchhiking of nanoparticles for drug delivery.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2024 Jan;204:115143. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2023.115143. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2024. PMID: 38008185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ionic liquids and their potential use in development and improvement of drug delivery systems: evidence of their tendency to promote drug accumulation in the brain.Pharm Dev Technol. 2024 Dec;29(10):1065-1074. doi: 10.1080/10837450.2024.2417004. Epub 2024 Oct 18. Pharm Dev Technol. 2024. PMID: 39403783 Review.
-
Glyco Ionic Liquids as Novel Nanoparticle Coatings to Enhance Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Drug Delivery.Adv Healthc Mater. 2025 Jul 9:e2500592. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202500592. Online ahead of print. Adv Healthc Mater. 2025. PMID: 40635271
-
Neuroinflammation, Blood-Brain Barrier, and HIV Reservoirs in the CNS: An In-Depth Exploration of Latency Mechanisms and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies.Viruses. 2025 Apr 16;17(4):572. doi: 10.3390/v17040572. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40285014 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fois A. F., Brew B. J., Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2015, 12, 299. - PubMed
-
- Liu R., Yeh Y.‐H. J., Varabyou A., Collora J. A., Sherrill‐Mix S., Talbot C. C., Mehta S., Albrecht K., Hao H., Zhang H., Pollack R. A., Beg S. A., Calvi R. M., Hu J., Durand C. M., Ambinder R. F., Hoh R., Deeks S. G., Chiarella J., Spudich S., Douek D. C., Bushman F. D., Pertea M., Ho Y.‐C., Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaz0802. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1726880/National Science Foundation
- Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America Foundation (PhRMA)
- P30GM122733/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM122733/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM130460/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 2236629/National Science Foundation
- R21 GM103460/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01DA056875/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- G0315202198510166/Sigma Xi Grants in Aid of Research
- P20GM103460/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- University of Mississippi iDRUM Initiative
- R01 DA056875/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- College of Liberal Arts at the University of Mississippi
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
