A phase I study of pevonedistat, azacitidine, and venetoclax in patients with relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 38572562
- PMCID: PMC11367232
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2024.285014
A phase I study of pevonedistat, azacitidine, and venetoclax in patients with relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
Azacitidine/venetoclax is an active regimen in patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML). However, primary or secondary resistance to azacitidine/venetoclax is an area of unmet need and overexpression of MCL1 is suggested to be a potential resistance mechanism. Pevonedistat inhibits MCL1 through activation of NOXA, and pevonedistat/azacitidine has previously shown activity in AML. To assess the tolerability and efficacy of adding pevonedistat to azacitidine/ venetoclax in relapsed/refractory AML, we conducted a phase I, multicenter, open-label study in 16 adults with relapsed/ refractory AML. Patients were treated with azacitidine, venetoclax along with pevonedistat intravenously on days 1, 3 and 5 of each 28-day cycle at doses of 10, 15 or 20 mg/m2 in successive cohorts in the dose escalation phase. The impact of treatment on protein neddylation as well as expression of pro-apoptotic BCL2 family members was assessed. The recommended phase II dose of pevonedistat was 20 mg/m2. Grade 3 or higher adverse events included neutropenia (31%), thrombocytopenia (13%), febrile neutropenia (19%), anemia (19%), hypertension (19%) and sepsis (19%). The overall response rate was 46.7% for the whole cohort including complete remission in five of seven (71.4%) patients who had not previously been treated with the hypomethylating agent/venetoclax. No measurable residual disease was detected in 80.0% of the patients who achieved complete remission. The median time to best response was 50 (range, 23-77) days. Four patients were bridged to allogeneic stem cell transplantation. The combination of azacitidine, venetoclax and pevonedistat is safe and shows encouraging preliminary activity in patients with relapsed/refractory AML. (NCT04172844).
Figures
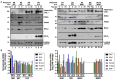
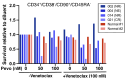

References
-
- DiNardo CD, Stein EM, de Botton S, et al. . Durable remissions with ivosidenib in IDH1-mutated relapsed or refractory AML. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(25):2386-2398. - PubMed
-
- Perl AE, Martinelli G, Cortes JE, et al. . Gilteritinib or chemotherapy for relapsed or refractory FLT3-mutated AML. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(18):1728-1740. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

