The Pharmacological Landscape for Fatty Change of the Pancreas
- PMID: 38573485
- PMCID: PMC11101365
- DOI: 10.1007/s40265-024-02022-7
The Pharmacological Landscape for Fatty Change of the Pancreas
Abstract
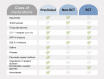
The quest for medications to reduce intra-pancreatic fat deposition is now quarter a century old. While no specific medication has been approved for the treatment of fatty change of the pancreas, drug repurposing shows promise in reducing the burden of the most common disorder of the pancreas. This leading article outlines the 12 classes of medications that have been investigated to date with a view to reducing intra-pancreatic fat deposition. Information is presented hierarchically-from preclinical studies to retrospective findings in humans to prospective interventional studies to randomised controlled trials. This lays the grounds for shepherding the most propitious drugs into medical practice through well-designed basic science studies and adequately powered randomised controlled trials.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.S.P. has no conflicts to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Clinical Implications of Fatty Pancreas: A Concise Review.Dig Dis Sci. 2017 Oct;62(10):2658-2667. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4700-1. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Dig Dis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28791556 Review.
-
Comprehensive analysis of dyslipidemia states associated with fat in the pancreas.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2023 Nov;17(11):102881. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2023.102881. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2023. PMID: 37862954
-
Fatty Pancreas: Should We Be Concerned?Pancreas. 2017 Nov/Dec;46(10):1251-1258. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000941. Pancreas. 2017. PMID: 29040194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Pancreas by Endoscopic Ultrasonography.Pancreas. 2019 Oct;48(9):1220-1224. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001396. Pancreas. 2019. PMID: 31593012
-
Enlarged pancreas: not always a cancer.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2015 Feb;14(1):107-8. doi: 10.1016/s1499-3872(15)60329-0. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2015. PMID: 25655299
Cited by
-
Fatty Pancreas: Its Potential as a Risk Factor for Pancreatic Cancer and Clinical Implications.Cancers (Basel). 2025 May 24;17(11):1765. doi: 10.3390/cancers17111765. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40507246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Metabolic Bariatric Surgery on Intra-pancreatic Fat Deposition and Total Pancreas Volume: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Obes Surg. 2025 Apr;35(4):1513-1524. doi: 10.1007/s11695-025-07778-9. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Obes Surg. 2025. PMID: 40097776 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-Pancreatic Fat Deposition and Pancreatitis: Insights from the COSMOS Program.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025 May 7;18:1489-1500. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S400276. eCollection 2025. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025. PMID: 40356715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship of Fat Deposition in the Liver and Pancreas with Cholecystectomy.Obes Facts. 2025 Apr 10:1-13. doi: 10.1159/000545781. Online ahead of print. Obes Facts. 2025. PMID: 40209687 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of high-density lipoprotein subfractions and apolipoprotein A-I with fat in the pancreas.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 Jan;27(1):123-133. doi: 10.1111/dom.15990. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025. PMID: 39377129 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

