Serum Biomarkers of Vascular Involvement in Childhood Uveitis
- PMID: 38573655
- PMCID: PMC11005069
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.13.4.9
Serum Biomarkers of Vascular Involvement in Childhood Uveitis
Abstract
Purpose: Nonanterior uveitis frequently involves the retinal vasculature; however, no molecular markers associated with the retinal vascular disease are currently known. In this study, we aimed to identify serum biomarker signatures associated with retinal vascular involvement in noninfectious pediatric uveitis.
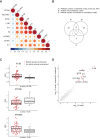
Methods: We performed a 384-plex targeted proteomic analysis of serum samples of 154 noninfectious pediatric uveitis patients diagnosed with nonanterior uveitis (n = 74), idiopathic chronic anterior uveitis (iCAU, n = 36), or juvenile idiopathic arthritis-associated uveitis (JIA-U, n = 44), as well as 22 noninflammatory pediatric controls. Data on retinal vascular involvement (i.e., papillitis, cystoid macular edema, retinal vasculitis, or retinal capillary leakage on optical coherence tomography and/or fluorescein angiography) were used to stratify cases in the nonanterior uveitis group.
Results: In the analysis of nonanterior uveitis, we identified nine proteins significantly associated with retinal vascular involvement, including F13B, MYOM3, and PTPN9. These proteins were enriched through pathway enrichment analysis for the coagulation cascade. Comparing cases and controls, we identified 63 differentially expressed proteins, notably proteins involved in platelet biology and complement cascades, which could be primarily attributed to differences in serum proteomes between anterior uveitis and nonanterior uveitis groups.
Conclusions: Serum proteins related to the coagulation and complement cascade are associated with retinal vascular involvement in pediatric uveitis patients. Our results indicate involvement of mediators that could interact with the microcirculation in pediatric uveitis and might serve as potential biomarkers in personalized medicine in the future.
Translational relevance: Our targeted proteomics analysis in serum of pediatric uveitis patients indicates involvement of mediators that could interact with the microcirculation in pediatric uveitis and might serve as potential biomarkers in personalized medicine in the future.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Prognostic value of antinuclear antibodies in juvenile idiopathic arthritis and anterior uveitis. Results from a systematic literature review.Acta Reumatol Port. 2014 Apr-Jun;39(2):116-22. Acta Reumatol Port. 2014. PMID: 24879943
-
MarkVCID cerebral small vessel consortium: I. Enrollment, clinical, fluid protocols.Alzheimers Dement. 2021 Apr;17(4):704-715. doi: 10.1002/alz.12215. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Alzheimers Dement. 2021. PMID: 33480172 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological therapies (remotely delivered) for the management of chronic and recurrent pain in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Mar 23;3(3):CD011118. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011118.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Apr 02;4:CD011118. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011118.pub3. PMID: 25803793 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cunningham J. Uveitis in children. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2000; 8(4): 251–261. - PubMed
-
- Yang P, Zhong Z, Su G, et al. .. Retinal vasculitis, a common manifestation of idiopathic pediatric uveitis? Retina. 2021; 41(3): 610–619. - PubMed
-
- Maleki A, Cao JH, Silpa-Archa S, Foster CS. Visual outcome and poor prognostic factors in isolated idiopathic retinal vasculitis. Retina. 2016; 36(10): 1979–1985. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

