Applications and Opportunities for Immune Cell CAR Engineering in Comparative Oncology
- PMID: 38573683
- PMCID: PMC11147717
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-3690
Applications and Opportunities for Immune Cell CAR Engineering in Comparative Oncology
Abstract
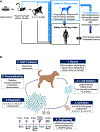
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-adoptive cell therapy has transformed the treatment of human hematologic malignancies. However, its application for the treatment of solid tumors remains challenging. An exciting avenue for advancing this field lies in the use of pet dogs, in which cancers that recapitulate the biology, immunological features, and clinical course of human malignancies arise spontaneously. Moreover, their large size, outbred genetic background, shared environment with humans, and immunocompetency make dogs ideal for investigating and optimizing CAR therapies before human trials. Here, we will outline how challenges in early clinical trials in patients with canine lymphoma, including issues related to autologous CAR T-cell manufacturing, limited CAR T-cell persistence, and tumor antigen escape, mirrored challenges observed in human CAR T trials. We will then highlight emerging adoptive cell therapy strategies currently under investigation in dogs with hematological and solid cancers, which will provide crucial safety and efficacy data on novel CAR T regimens that can be used to support clinical trials. By drawing from ongoing studies, we will illustrate how canine patients with spontaneous cancer may serve as compelling screening platforms to establish innovative CAR therapy approaches and identify predictive biomarkers of response, with a specific emphasis on solid tumors. With increased funding for canine immunotherapy studies, multi-institutional investigations are poised to generate highly impactful clinical data that should translate into more effective human trials, ultimately benefiting both human and canine cancer patients.
©2024 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune Cell Hacking: Challenges and Clinical Approaches to Create Smarter Generations of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells.Front Immunol. 2018 Jul 31;9:1717. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01717. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30108584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revolutionizing immunotherapy: The next frontier in CAR T-cell engineering.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2025 Jul;211:104751. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2025.104751. Epub 2025 Apr 28. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2025. PMID: 40306469 Review.
-
Oncolytic Viruses as Reliable Adjuvants in CAR-T Cell Therapy for Solid Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 16;25(20):11127. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011127. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering CAR-T Cells for Next-Generation Cancer Therapy.Cancer Cell. 2020 Oct 12;38(4):473-488. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.07.005. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Cancer Cell. 2020. PMID: 32735779 Review.
-
Chimeric antigen-receptor T-cell therapy for hematological malignancies and solid tumors: Clinical data to date, current limitations and perspectives.Curr Res Transl Med. 2017 Sep;65(3):93-102. doi: 10.1016/j.retram.2017.08.003. Curr Res Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28988742 Review.
Cited by
-
Intertumoral heterogeneity of the immune microenvironment in high grade canine mast cell tumors.Vet Oncol. 2025;2(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s44356-025-00020-9. Epub 2025 Mar 14. Vet Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40093350 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Gene Therapy with Oncolytic Viruses and CAR-T Cells and Therapy-Related Groups.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Apr 10;47(4):268. doi: 10.3390/cimb47040268. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in CAR optimization strategies based on CD28.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 13;16:1548772. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1548772. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40181986 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

