Chloride ions in health and disease
- PMID: 38573803
- PMCID: PMC11065649
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20240029
Chloride ions in health and disease
Abstract
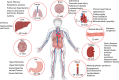
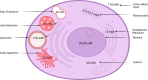
Chloride is a key anion involved in cellular physiology by regulating its homeostasis and rheostatic processes. Changes in cellular Cl- concentration result in differential regulation of cellular functions such as transcription and translation, post-translation modifications, cell cycle and proliferation, cell volume, and pH levels. In intracellular compartments, Cl- modulates the function of lysosomes, mitochondria, endosomes, phagosomes, the nucleus, and the endoplasmic reticulum. In extracellular fluid (ECF), Cl- is present in blood/plasma and interstitial fluid compartments. A reduction in Cl- levels in ECF can result in cell volume contraction. Cl- is the key physiological anion and is a principal compensatory ion for the movement of the major cations such as Na+, K+, and Ca2+. Over the past 25 years, we have increased our understanding of cellular signaling mediated by Cl-, which has helped in understanding the molecular and metabolic changes observed in pathologies with altered Cl- levels. Here, we review the concentration of Cl- in various organs and cellular compartments, ion channels responsible for its transportation, and recent information on its physiological roles.
Keywords: Anion transport; Chloride channels; Chloride ions; Chloride transporters; Ion homeostasis.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

