The effects of parental respect for children's decision-making and respect for human rights on depression in early adolescents: The mediating effect of self-esteem
- PMID: 38573997
- PMCID: PMC10994345
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300320
The effects of parental respect for children's decision-making and respect for human rights on depression in early adolescents: The mediating effect of self-esteem
Abstract
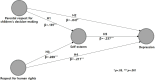
This study investigated the structural relationships among parental respect for children's decision-making, respect for human rights, and self-esteem, and their impact on depression in early adolescents. The study utilized data from 2,747 middle school students who participated in the 2020 Survey on the Current Status of Korean Children's and Youth's Rights conducted by the National Youth Policy Institute. The data were analyzed using a structural equation model based on partial least squares with SmartPLS 3.0. The analysis revealed that both parental respect for children's decision-making and respect for human rights perceived by middle school students had a significant positive impact on self-esteem and a significant negative impact on depression. Furthermore, self-esteem was found to have a significant negative effect on depression. Importantly, self-esteem also played a significant mediating role in the relationship between parental respect for children's decision-making and depression, as well as the relationship between respect for human rights and depression. Therefore, in order to manage depression, it is necessary to develop strategies that encourage parental respect for children's decision-making, promote respect for human rights, and foster self-esteem in early adolescents.
Copyright: © 2024 Sangmi Lee. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Moderating Effect of Human Rights Education: Examining the Relationship Between Parental Abuse, Child Self-Esteem, and Human Rights Attitude.J Interpers Violence. 2025 May;40(9-10):2331-2355. doi: 10.1177/08862605241270014. Epub 2024 Aug 13. J Interpers Violence. 2025. PMID: 39135483
-
[The Influence of Parental Self-Esteem on Late School-Aged Children's Media Device Addiction: The Mediating Effect of Marital Conflict and Children's Self-Esteem].J Korean Acad Nurs. 2022 Aug;52(4):421-434. doi: 10.4040/jkan.22036. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2022. PMID: 36117303 Korean.
-
Family Income and Child Depression: The Chain Mediating Effect of Parental Involvement, Children's Self-Esteem, and Group Differences.Children (Basel). 2024 Apr 16;11(4):478. doi: 10.3390/children11040478. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38671695 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of social withdrawal and depression on the self-esteem of female adolescents: The mediating effect of grit.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 12;18(7):e0288530. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288530. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37437061 Free PMC article.
-
Children patients with COVID-19: How can parental and peer support lessen the psychological burden of isolation.Nurs Open. 2023 Nov;10(11):7118-7129. doi: 10.1002/nop2.1972. Epub 2023 Aug 26. Nurs Open. 2023. PMID: 37632315 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ministry of Education Kora Disease Control and Agency Prevention. 2022. Announcement of student health examination and youth health behavior survey results [Internet]. 2023 Apr 14 [cited 9 Nov 2023]. Available from: https://www.moe.go.kr/boardCnts/viewRenew.do?boardID=294&boardSeq=94695&....
-
- Kim YJ, Hwang SY, Choi HG. 2020 Implementation Study of the International Convention on the Rights of Children and Adolescents—The Human Rights Situation of Children and Adolescents in Korea: Basic Analysis Report. Sejong: Korea Youth Policy Institute; 2020.
-
- Son WJ, Bae SM. The relationship between human rights, negative affect, bullying victimization, and life satisfaction among Korean adolescents: A national sample study. Child Youth Serv Rev. 2022;139: 106568. doi: 10.1016/j.childyouth.2022.106568 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical