Health state utility values ranges across varying stages and severity of type 2 diabetes-related complications: A systematic review
- PMID: 38574169
- PMCID: PMC10994347
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297589
Health state utility values ranges across varying stages and severity of type 2 diabetes-related complications: A systematic review
Abstract
Introduction: Health state utility values (HSUV) for Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) complications are useful in economic evaluations to determine cost effectiveness of an intervention. However, there is a lack of reference ranges for different severity and stages of individual complications. This study aimed to provide an overview of HSUV decrement ranges for common T2DM complications focusing on different severity and stages of complications.
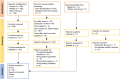
Method: A systematic search was conducted in MEDLINE, SCOPUS, WEB OF SCIENCE. (Jan 2000 to April 2022). Included studies for HSUV estimates were from outpatient setting, regardless of treatment types, complication stages, regions and HRQoL instruments. Health Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) outcomes was to be presented as HSUV decrement values, adjusted according to social demographics and comorbidities. Adjusted HSUV decrements were extracted and compiled according to individual complications. After which, subsequently grouped into mild or severe category for comparison.
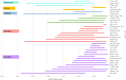
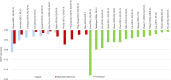
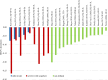
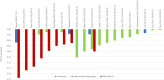
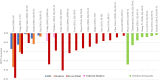
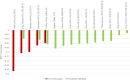
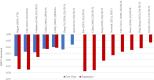
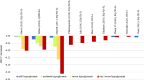
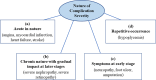
Results: Searches identified 35 studies. The size of the study population ranged from 160 to 14,826. The HSUV decrement range was widest for cerebrovascular disease (stroke): -0.0060 to -0.0780 for mild stroke and -0.035 to -0.266 for severe stroke; retinopathy: mild (-0.005 to -0.0862), moderate (-0.0030 to -0.1845) and severe retinopathy (-0.023 to -0.2434); amputation: (-0.1050 to -0.2880). Different nature of complication severity defined in studies could be categorized into: those with acute nature, chronic with lasting effects, those with symptoms at early stage or those with repetitive frequency or episodes.
Discussion: Overview of HSUV decrement ranges across different stages of each T2DM diabetes-related complications shows that chronic complications with lasting impact such as amputation, severe stroke with sequelae and severe retinopathy with blindness were generally associated with larger HSUV decrement range. Considerable heterogeneities exist across the studies. Promoting standardized complication definitions and identifying the most influential health state stages on HSUV decrements may assist researchers for future cost-effectiveness studies.
Copyright: © 2024 Tan et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Health state utility values of type 2 diabetes mellitus and related complications: a systematic review and meta-regression.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2024 Sep 7;22(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12955-024-02288-1. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2024. PMID: 39244536 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying health-related quality of life in Malaysian type 2 diabetes: focusing on complication types and severity.Qual Life Res. 2023 Jul;32(7):1925-1941. doi: 10.1007/s11136-023-03360-x. Epub 2023 Feb 13. Qual Life Res. 2023. PMID: 36781810
-
Health state utility values for diabetic retinopathy: protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis.Syst Rev. 2015 Feb 21;4:15. doi: 10.1186/s13643-015-0006-6. Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25875206 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioural modification interventions for medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(46):1-490. doi: 10.3310/hta24460. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32975190 Free PMC article.
-
The validity of the SF-12 and SF-6D instruments in people living with HIV/AIDS in Kenya.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017 Jul 17;15(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s12955-017-0708-7. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017. PMID: 28716065 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organisation. 2021. Available: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases
-
- American Diabetes Association. 2022. Available: https://diabetes.org/about-us/statistics/cost-diabetes
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

