Does the use of higher versus lower oxygen concentration improve neurodevelopmental outcomes at 18-24 months in very low birthweight infants?
- PMID: 38576007
- PMCID: PMC10996184
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-024-08080-2
Does the use of higher versus lower oxygen concentration improve neurodevelopmental outcomes at 18-24 months in very low birthweight infants?
Abstract
Background: Immediately after birth, the oxygen saturation is between 30 and 50%, which then increases to 85-95% within the first 10 min. Over the last 10 years, recommendations regarding the ideal level of the initial fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) for resuscitation in preterm infants have changed from 1.0, to room air to low levels of oxygen (< 0.3), up to moderate concentrations (0.3-0.65). This leaves clinicians in a challenging position, and a large multi-center international trial of sufficient sample size that is powered to look at safety outcomes such as mortality and adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes is required to provide the necessary evidence to guide clinical practice with confidence.
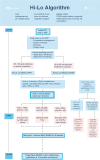
Methods: An international cluster, cross-over randomized trial of initial FiO2 of 0.3 or 0.6 during neonatal resuscitation in preterm infants at birth to increase survival free of major neurodevelopmental outcomes at 18 and 24 months corrected age will be conducted. Preterm infants born between 230/7 and 286/7 weeks' gestation will be eligible. Each participating hospital will be randomized to either an initial FiO2 concentration of either 0.3 or 0.6 to recruit for up to 12 months' and then crossed over to the other concentration for up to 12 months. The intervention will be initial FiO2 of 0.6, and the comparator will be initial FiO2 of 0.3 during respiratory support in the delivery room. The sample size will be 1200 preterm infants. This will yield 80% power, assuming a type 1 error of 5% to detect a 25% reduction in relative risk of the primary outcome from 35 to 26.5%. The primary outcome will be a composite of all-cause mortality or the presence of a major neurodevelopmental outcome between 18 and 24 months corrected age. Secondary outcomes will include the components of the primary outcome (death, cerebral palsy, major developmental delay involving cognition, speech, visual, or hearing impairment) in addition to neonatal morbidities (severe brain injury, bronchopulmonary dysplasia; and severe retinopathy of prematurity).
Discussion: The use of supplementary oxygen may be crucial but also potentially detrimental to preterm infants at birth. The HiLo trial is powered for the primary outcome and will address gaps in the evidence due to its pragmatic and inclusive design, targeting all extremely preterm infants. Should 60% initial oxygen concertation increase survival free of major neurodevelopmental outcomes at 18-24 months corrected age, without severe adverse effects, this readily available intervention could be introduced immediately into clinical practice.
Trial registration: The trial was registered on January 31, 2019, at ClinicalTrials.gov with the Identifier: NCT03825835.
Keywords: Delivery room; Extremely preterm; Infant; Neonatal intensive care; Neonatal mortality; Oxygen.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Similar articles
-
Intratracheal budesonide mixed with surfactant to increase survival free of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in extremely preterm infants: study protocol for the international, multicenter, randomized PLUSS trial.Trials. 2023 May 9;24(1):320. doi: 10.1186/s13063-023-07257-5. Trials. 2023. PMID: 37161488 Free PMC article.
-
Mortality, In-Hospital Morbidity, Care Practices, and 2-Year Outcomes for Extremely Preterm Infants in the US, 2013-2018.JAMA. 2022 Jan 18;327(3):248-263. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.23580. JAMA. 2022. PMID: 35040888 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical analysis plan for the FiO2-C trial: effects of closed-loop automatic control of the inspiratory fraction of oxygen (FiO2-C) on outcomes of extremely preterm infants-a randomized-controlled parallel group multicentre trial for safety and efficacy.Trials. 2024 Nov 12;25(1):756. doi: 10.1186/s13063-024-08615-7. Trials. 2024. PMID: 39533330 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of different protein concentrations of human milk fortifier for promoting growth and neurological development in preterm infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 20;11(11):CD007090. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007090.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33215474 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol in preterm infants at risk for or having respiratory distress syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jul 8;7(7):CD000366. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000366.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31283839 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Neurodevelopmental Outcomes of Very Low Birth Weight Infants Following Extrauterine Placental Perfusion: A Follow-Up Study.Acta Paediatr. 2025 Sep;114(9):2246-2252. doi: 10.1111/apa.70101. Epub 2025 Apr 18. Acta Paediatr. 2025. PMID: 40251781 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Wyckoff MH, Wyllie JP, Aziz K, de Almeida MF, Fabres J, Fawke J, et al. Neonatal Life Support: 2020 International Consensus on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science With Treatment Recommendations. Circulation. 2020;142:329–337. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000895. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical