Synthetic biology-based bacterial extracellular vesicles displaying BMP-2 and CXCR4 to ameliorate osteoporosis
- PMID: 38576241
- PMCID: PMC10995478
- DOI: 10.1002/jev2.12429
Synthetic biology-based bacterial extracellular vesicles displaying BMP-2 and CXCR4 to ameliorate osteoporosis
Erratum in
-
Correction to "Synthetic Biology-Based Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles Displaying BMP-2 and CXCR4 to Ameliorate Osteoporosis".J Extracell Vesicles. 2025 Jun;14(6):e70095. doi: 10.1002/jev2.70095. J Extracell Vesicles. 2025. PMID: 40452467 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
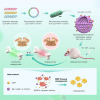
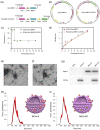
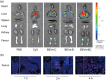
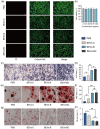
Osteoporosis (OP) is a systematic bone disease characterized by low bone mass and fragile bone microarchitecture. Conventional treatment for OP has limited efficacy and long-term toxicity. Synthetic biology makes bacterial extracellular vesicle (BEVs)-based therapeutic strategies a promising alternative for the treatment of OP. Here, we constructed a recombinant probiotics Escherichia coli Nissle 1917-pET28a-ClyA-BMP-2-CXCR4 (ECN-pClyA-BMP-2-CXCR4), in which BMP-2 and CXCR4 were overexpressed in fusion with BEVs surface protein ClyA. Subsequently, we isolated engineered BEVs-BMP-2-CXCR4 (BEVs-BC) for OP therapy. The engineered BEVs-BC exhibited great bone targeting in vivo. In addition, BEVs-BC had good biocompatibility and remarkable ability to promote osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. Finally, the synthetic biology-based BEVs-BC significantly prevented the OP in an ovariectomized (OVX) mouse model. In conclusion, we constructed BEVs-BC with both bone-targeting and bone-forming in one-step using synthetic biology, which provides an effective strategy for OP and has great potential for industrialization.
Keywords: bacterial extracellular vesicle; bone targeting; osteogenic differentiation; osteoporosis; synthetic biology.
© 2024 The Authors. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kim, H. Y. , Song, M. K. , Gho, Y. S. , Kim, H. H. , & Choi, B. K. (2021). Extracellular vesicles derived from the periodontal pathogen Filifactor alocis induce systemic bone loss through Toll‐like receptor 2. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 10(12), e12157. 10.1002/jev2.12157 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee, K. S. , Lee, J. , Kim, H. K. , Yeom, S. H. , Woo, C. H. , Jung, Y. J. , Yun, Y. E. , Park, S. Y. , Han, J. , Kim, E. , Sul, J. H. , Jung, J. M. , Park, J. H. , Choi, J. S. , Cho, Y. W. , & Jo, D.‐G. (2021). Extracellular vesicles from adipose tissue‐derived stem cells alleviate osteoporosis through osteoprotegerin and miR‐21‐5p. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 10(12), e12152. 10.1002/jev2.12152 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- SUTIM-202303;SUTIM-2023006/Foundation of National Center for Translational Medicine (Shanghai) SHU Branch
- GZB20230397/National Postdoctoral Researcher Program
- 92249303/Integrated Project of Major Research Plan of National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 23141900600/Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology Laboratory Animal Research Project
- 82202344;82230071/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

