Isolation and purification of polysaccharides from Bupleurum marginatum Wall.ex DC and their anti-liver fibrosis activities
- PMID: 38576476
- PMCID: PMC10991770
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1342638
Isolation and purification of polysaccharides from Bupleurum marginatum Wall.ex DC and their anti-liver fibrosis activities
Abstract
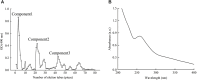
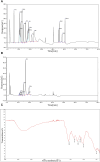
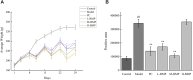
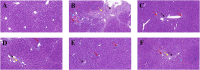
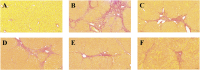
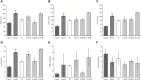
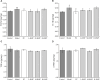
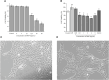
Bupleurum marginatum Wall.ex DC [Apiaceae] (BM)is widely grown in southwestern China, and the whole plant is used as Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). Polysaccharides are main natural products in lots of TCM and have been studied for their effects of reducing oxidative stress, anti-inflammation and immune regulation. Herein, we investigated the extraction techniques of Bupleurum marginatum Wall.ex DC polysaccharides (BMP), the identification of their key components, and their ability to inhibit liver fibrosis in both cellular and animal models. Component identification indicated that monosaccharides in BMP mainly consisted of glucose, galactose, mannose, rhamnose, arabinose, and xylose. In vivo analysis revealed that BMP provided significant protective effects on N-Nitroso dimethylamine (NDMA)-induced liver fibrosis rats through reducing hepatomegaly, reducing tissue inflammation, and reducing collagen deposition. BMP also improved the hepatobiliary system and liver metabolism in accord to reduce the serum levels of ALT, AST, ALP, r-GT, and TBIL. In addition, BMP could reduce the level of inflammation and fibrosis through inhibition of IL-1β and TGF-β1. Cellular studies showed that the BMP could provide therapeutic effects on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced cellular fibrosis model, and could reduce the level of inflammation and fibrosis by decreasing the level of TGF-β1, IL-1β, and TNF-α. Our study demonstrated that BMP may provide a new therapy strategy of liver injury and liver fibrosis.
Keywords: Bupleurum marginatum Wall.ex DC; activity study; anti-liver fibrosis; polysaccharides; water extraction and alcohol precipitation.
Copyright © 2024 Xiao, Sunniya, Li, Kakar, Dai and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ashour M. L., Youssef F. S., Gad H. A., El-Readi M. Z., Bouzabata A., Abuzeid R. M., et al. (2018). Evidence for the anti-inflammatory activity of Bupleurum marginatum (Apiaceae) extracts using in vitro and in vivo experiments supported by virtual screening. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 70 (7), 952–963. 10.1111/jphp.12904 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cai F. F., Bian Y. Q., Wu R., Sun Y., Chen X. L., Yang M. D., et al. (2019a). Yinchenhao decoction suppresses rat liver fibrosis involved in an apoptosis regulation mechanism based on network pharmacology and transcriptomic analysis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 114, 108863. 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108863 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

