The ethnomedicine, phytochemistry, and pharmacological properties of the genus Bersama: current review and future perspectives
- PMID: 38576479
- PMCID: PMC10991763
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1366427
The ethnomedicine, phytochemistry, and pharmacological properties of the genus Bersama: current review and future perspectives
Abstract
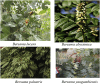
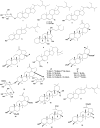
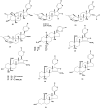
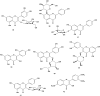
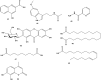
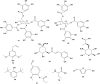
Bersama (Melianthaceae) has been used in traditional medicine for a wide range of ailments, including blood purifier, immune booster, psychotropic medication, and treatment for malaria, hepatitis, infertility, diabetes, impotency, meningitis, and stroke. This review gathers fragmented information from the literature on ethnomedicinal applications, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology of the Bersama genus. It also explores the therapeutic potential of the Bersama genus in ethnophytopharmacology, allowing for further investigation. All the available information published in the English language on Bersama genus was compiled from electronic databases such as Academic Journals, Ethnobotany, Google Scholar, PubMed, Science Direct, Web of Science, and library search using the following keywords: "Bersama genus," "traditional use," "phytochemistry," "pharmacological effects," and "toxicology". The ethnomedical applications of the Bersama genus have been recorded, and it has been used traditionally for more than 30 different types of ailments. Thus far, more than 50 compounds have been isolated from the genus. Cardiac glycosides and terpenoids are the main compounds isolated from the Bersama genus. Different plant parts of Bersama genus extracts demonstrated a wide range of pharmacological properties, including antioxidant, antimalarial, antidiabetic, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and cytotoxic activity. Exemplary drug leads from the genus include mangiferin and quercetin-3-O-arabinopyranoside, both of which have antioxidant activities. Bersama genus has long been used to cure a wide range of ailments. Bersama genus extracts and phytochemicals have been found to have promising pharmacological activities. Further study on promising crude extracts and compounds is required to develop innovative therapeutic candidates.
Keywords: Bersama genus; antidiabetic; antimalarial; antioxidant; antiviral; cytotoxic; mangiferin; quercetin-3-O-araiopyraoside.
Copyright © 2024 Nigussie, Ashenef and Meresa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comprehensive review of the ethnomedicine, phytochemistry, pharmacological activities of the genus Kniphofia.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):1177-1189. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2085753. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 35701101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethnobotany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology of the genus Sambucus L. (Viburnaceae).J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jun 28;292:115102. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115102. Epub 2022 Mar 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35288288 Review.
-
Ethnopharmacological uses, phytochemistry, biological activities, and therapeutic applications of Clinacanthus nutans (Burm. f.) Lindau: A comprehensive review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Jul 12;206:245-266. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.05.007. Epub 2017 May 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28495603 Review.
-
Traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Ficus carica: a review.Pharm Biol. 2014 Nov;52(11):1487-503. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2014.892515. Epub 2014 Jul 14. Pharm Biol. 2014. PMID: 25017517 Review.
-
A review on ethnobotany, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of the genus Didymocarpus wall. (Gesneriaceae).J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Sep 15;295:115404. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115404. Epub 2022 May 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35643208 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiac glycosides: Looking beyond heart failure and atrial fibrillation.Indian J Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 1;57(1):33-47. doi: 10.4103/ijp.ijp_934_24. Epub 2025 May 6. Indian J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40324829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acharyulu N., Dubey R., Swaminadham V., Kollu P., Kalyani R., Pammi S. (2014). Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles using Phyllanthus amarus leaf extract and their antibacterial activity against multidrug resistance bacteria. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 3, 639–641.
-
- Agidew M. (2022). Phytochemical analysis of some selected traditional medicinal plants in Ethiopia. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 46, 87–22. 10.1186/s42269-022-00770-8 - DOI
-
- Ajao A., Sibiya N., Moteetee A. (2019). Sexual prowess from nature: a systematic review of medicinal plants used as aphrodisiacs and sexual dysfunction in sub-Saharan Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 122, 342–359. 10.1016/j.sajb.2018.08.011 - DOI
-
- Alehegn A. A., Yesuf J. S., Birru E. M. (2020). Antimalarial activity of crude extract and solvent fractions of the leaves of Bersama abyssinica Fresen.(Melianthaceae) against Plasmodium berghei infection in Swiss albino mice. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 9467359. 10.1155/2020/9467359 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

