Efficacy and safety of Panax notoginseng saponin injection in the treatment of acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 38576488
- PMCID: PMC10991745
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1353662
Efficacy and safety of Panax notoginseng saponin injection in the treatment of acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
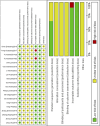
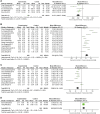
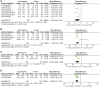
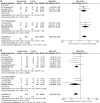
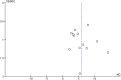
Purpose: This study aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of Panax notoginseng saponin (PNS) injection, when combined with conventional treatment (CT), for acute myocardial infarction (AMI). Methods: Comprehensive searches were conducted in seven databases from inception until 28 September 2023. The search aimed to identify relevant randomized controlled trials (RCTs) focusing on PNS injection in the context of AMI. This meta-analysis adhered to the PRISMA 2020 guidelines, and its protocol was registered with PROSPERO (number: CRD42023480131). Result: Twenty RCTs involving 1,881 patients were included. The meta-analysis revealed that PNS injection, used adjunctively with CT, significantly improved treatment outcomes compared to CT alone, as evidenced by the following points: (1) enhanced total effective rate [OR = 3.09, p < 0.05]; (2) decreased incidence of major adverse cardiac events [OR = 0.32, p < 0.05]; (3) reduction in myocardial infarct size [MD = -6.53, p < 0.05]; (4) lower ST segment elevation amplitude [MD = -0.48, p < 0.05]; (5) mitigated myocardial injury as indicated by decreased levels of creatine kinase isoenzymes [MD = -11.19, p < 0.05], cardiac troponin T [MD = -3.01, p < 0.05], and cardiac troponin I [MD = -10.72, p < 0.05]; (6) enhanced cardiac function, reflected in improved brain natriuretic peptide [MD = -91.57, p < 0.05], left ventricular ejection fraction [MD = 5.91, p < 0.05], left ventricular end-diastolic dimension [MD = -3.08, p < 0.05], and cardiac output [MD = 0.53, p < 0.05]; (7) reduced inflammatory response, as shown by lower levels of C-reactive protein [MD = -2.99, p < 0.05], tumor necrosis factor-α [MD = -6.47, p < 0.05], interleukin-6 [MD = -24.46, p < 0.05], and pentraxin-3 [MD = -2.26, p < 0.05]; (8) improved vascular endothelial function, demonstrated by decreased endothelin-1 [MD = -20.56, p < 0.05] and increased nitric oxide [MD = 1.33, p < 0.05]; (9) alleviated oxidative stress, evidenced by increased superoxide dismutase levels [MD = 25.84, p < 0.05]; (10) no significant difference in adverse events [OR = 1.00, p = 1.00]. Conclusion: This study highlighted the efficacy and safety of adjunctive PNS injections in enhancing AMI patient outcomes beyond CT alone. Future RCTs need to solidify these findings through rigorous methods. Systematic Review Registration: (https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/), identifier (CRD42023480131).
Keywords: Panax notoginseng saponins; acute myocardial infarction; meta-analysis; randomized controlled trials; systematic review.
Copyright © 2024 Chen, Gao, Guo, Pan, Zhang, Du and Shi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





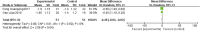


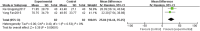




Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of salvianolate injection in treating acute myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis and systematic literature review.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 17;15:1478558. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1478558. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39741628 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of puerarin injection as an adjunctive therapy for chronic heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 28;16:1516059. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1516059. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40391374 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Astragalus membranaceus on left ventricular remodeling in HFrEF: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 12;15:1345797. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1345797. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38283626 Free PMC article.
-
Panax notoginseng preparation plus aspirin versus aspirin alone on platelet aggregation and coagulation in patients with coronary heart disease or ischemic stroke: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 7;13:1015048. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1015048. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36569332 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine injections with Tonifying Qi, equivalent effect of regulating energy metabolism, for acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 28;16:1511486. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1511486. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40223935 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
FOS as a biomarker for myocardial infarction treatment with Deng's Yangxin Decoction: a systems biology-based analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 May 30;12:1488684. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1488684. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40520937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen J., Xue R., Li L., Xiao L. L., Shangguan J., Zhang W., et al. (2019). Panax notoginseng saponins protect cardiac myocytes against endoplasmic reticulum stress and associated apoptosis through mediation of intracellular calcium homeostasis. Front. Pharmacol. 10, 1013. 10.3389/fphar.2019.01013 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen Z. (2019). Effect of Xuesaitong injection on myocardial injury and cardiac function in patients with acute ST segment elevation myocardial infarction. Xizang Med. (01), 145–147.
-
- Dai L., Zhang Y., Jiang Y., Chen K. (2022). Panax notoginseng preparation plus aspirin versus aspirin alone on platelet aggregation and coagulation in patients with coronary heart disease or ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 1015048. 10.3389/fphar.2022.1015048 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

