In silico identification of compounds from Piper sarmentosum Roxb leaf fractionated extract inhibit interleukin-6 to prevent rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 38576490
- PMCID: PMC10991700
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1358037
In silico identification of compounds from Piper sarmentosum Roxb leaf fractionated extract inhibit interleukin-6 to prevent rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
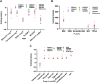
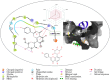
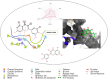
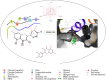
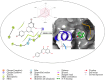
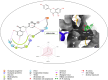
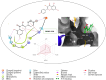
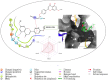
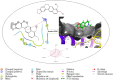
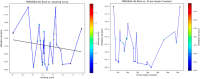
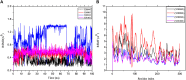
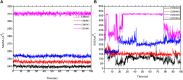
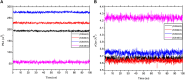
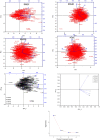
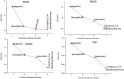
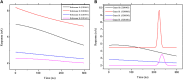
Objective: Medicinal herbs with a phytonutrient background has been applied globally as major alternatives to ameliorate the continuous increase in rheumatoid arthritis cases worldwide. We herein aimed to critically examine the bioactive components of the medicinal herb Piper sarmentosum Roxb leaf fractionated extract for its potential to inhibit the influx of interleukin-6 (IL-6) in rheumatoid arthritis. Methods: The Schrödinger platform was employed as the main computational acumen for the screening of bioactive compounds identified and reference compounds subjected to molecular simulation (MDS) for analyzing the stability of docked complexes to assess fluctuations and conformational changes during protein-ligand interactions. Results: The values of the simulatory properties and principal component analysis (PCA) revealed the good stability of these phytochemicals in the active pocket of interleukin-6 (IL-6). Discussion: Our findings reveal new strategies in which these phytochemicals are potential inhibitory agents that can be modified and further evaluated to develop more effective agents for the management of rheumatoid arthritis, thereby providing a better understanding and useful model for the reproduction and/or discovery of new drugs for the management of rheumatoid arthritis and its complications.
Keywords: conformational; interleukin-6; phytonutrient; rheumatoid arthritis; simulation.
Copyright © 2024 Dao, Onikanni, Fadaka, Klein, Tran, Le, Wang and Chang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phytotherapeutic potential of compounds identified from fractionated extracts of Morus alba L., as an inhibitor of interleukin-6 in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: computational approach.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024 Mar 25:1-14. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2024.2330713. Online ahead of print. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024. PMID: 38525928
-
Piper sarmentosum Roxb.: A review on its botany, traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacological activities.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Dec 5;263:112897. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112897. Epub 2020 Jul 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32620264 Review.
-
Effect of Piper chaba Hunter, Piper sarmentosum Roxb. and Piper interruptum Opiz. on natural killer cell activity and lymphocyte proliferation.J Med Assoc Thai. 2014 Aug;97 Suppl 8:S133-9. J Med Assoc Thai. 2014. PMID: 25518305
-
Bioactive compounds and therapeutic role of Brassica oleracea L. seeds in rheumatoid arthritis rats via regulating inflammatory signalling pathways and antagonizing interleukin-1 receptor action.Biomarkers. 2021 Dec;26(8):788-807. doi: 10.1080/1354750X.2021.1999504. Biomarkers. 2021. PMID: 34704882
-
Effects of Piper sarmentosum Roxb. on hypertension and diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 25;13:976247. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.976247. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36091787 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

