Nomogram based on multimodal magnetic resonance combined with B7-H3mRNA for preoperative lymph node prediction in esophagus cancer
- PMID: 38576593
- PMCID: PMC10989267
- DOI: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i3.419
Nomogram based on multimodal magnetic resonance combined with B7-H3mRNA for preoperative lymph node prediction in esophagus cancer
Abstract
Background: Accurate preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis (LNM) in esophageal cancer (EC) patients is of crucial clinical significance for treatment planning and prognosis.
Aim: To develop a clinical radiomics nomogram that can predict the preoperative lymph node (LN) status in EC patients.
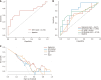
Methods: A total of 32 EC patients confirmed by clinical pathology (who underwent surgical treatment) were included. Real-time fluorescent quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction was used to detect the expression of B7-H3 mRNA in EC tissue obtained during preoperative gastroscopy, and its correlation with LNM was analyzed. Radiomics features were extracted from multi-modal magnetic resonance imaging of EC using Pyradiomics in Python. Feature extraction, data dimensionality reduction, and feature selection were performed using XGBoost model and leave-one-out cross-validation. Multivariable logistic regression analysis was used to establish the prediction model, which included radiomics features, LN status from computed tomography (CT) reports, and B7-H3 mRNA expression, represented by a radiomics nomogram. Receiver operating characteristic area under the curve (AUC) and decision curve analysis (DCA) were used to evaluate the predictive performance and clinical application value of the model.
Results: The relative expression of B7-H3 mRNA in EC patients with LNM was higher than in those without metastasis, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). The AUC value in the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was 0.718 (95%CI: 0.528-0.907), with a sensitivity of 0.733 and specificity of 0.706, indicating good diagnostic performance. The individualized clinical prediction nomogram included radiomics features, LN status from CT reports, and B7-H3 mRNA expression. The ROC curve demonstrated good diagnostic value, with an AUC value of 0.765 (95%CI: 0.598-0.931), sensitivity of 0.800, and specificity of 0.706. DCA indicated the practical value of the radiomics nomogram in clinical practice.
Conclusion: This study developed a radiomics nomogram that includes radiomics features, LN status from CT reports, and B7-H3 mRNA expression, enabling convenient preoperative individualized prediction of LNM in EC patients.
Keywords: B7-H3mRNA; Esophageal cancer; Lymph node metastasis; Multimodal magnetic resonance imaging; Nomogram; Radiomics.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A new approach to predict lymph node metastasis in solid lung adenocarcinoma: a radiomics nomogram.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Apr;10(Suppl 7):S807-S819. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.03.126. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 29780627 Free PMC article.
-
A clinical-radiomics nomogram for the preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer.J Transl Med. 2020 Jan 30;18(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02215-0. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32000813 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Nomogram Combining CT Imaging with Clinical Features for Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis in Stage I-IIIB Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.Ther Innov Regul Sci. 2022 Jan;56(1):155-167. doi: 10.1007/s43441-021-00345-1. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Ther Innov Regul Sci. 2022. PMID: 34699046
-
Radiomics diagnostic performance for predicting lymph node metastasis in esophageal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 Jun 12;24(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01278-5. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38867143 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging-radiomics in cervical cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 4;14:1416378. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1416378. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39026971 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Predicting preoperative lymph node metastasis in esophageal cancer: Advancement and challenges.World J Clin Oncol. 2025 Mar 24;16(3):102863. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i3.102863. World J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40130042 Free PMC article.
-
B7H3 in Gastrointestinal Tumors: Role in Immune Modulation and Cancer Progression: A Review of the Literature.Cells. 2025 Apr 2;14(7):530. doi: 10.3390/cells14070530. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40214484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Value of Computed Tomography Scan for Detecting Lymph Node Metastasis in Early Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Ann Surg Oncol. 2025 Mar;32(3):1635-1650. doi: 10.1245/s10434-024-16568-z. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Ann Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39586955
-
Radiomics in Oesogastric Cancer: Staging and Prediction of Preoperative Treatment Response: A Narrative Review and the Results of Personal Experience.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 26;16(15):2664. doi: 10.3390/cancers16152664. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123392 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–132. - PubMed
-
- Cooper JS, Guo MD, Herskovic A, Macdonald JS, Martenson JA Jr, Al-Sarraf M, Byhardt R, Russell AH, Beitler JJ, Spencer S, Asbell SO, Graham MV, Leichman LL. Chemoradiotherapy of locally advanced esophageal cancer: long-term follow-up of a prospective randomized trial (RTOG 85-01). Radiation Therapy Oncology Group. JAMA. 1999;281:1623–1627. - PubMed
-
- Visser E, van Rossum PSN, Ruurda JP, van Hillegersberg R. Impact of Lymph Node Yield on Overall Survival in Patients Treated With Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy Followed by Esophagectomy for Cancer: A Population-based Cohort Study in the Netherlands. Ann Surg. 2017;266:863–869. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

