Update on the reciprocal interference between immunosuppressive therapy and gut microbiota after kidney transplantation
- PMID: 38576749
- PMCID: PMC10989467
- DOI: 10.5500/wjt.v14.i1.90194
Update on the reciprocal interference between immunosuppressive therapy and gut microbiota after kidney transplantation
Abstract
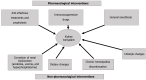
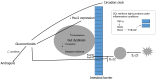
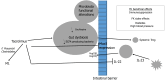
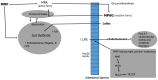
Gut microbiota is often modified after kidney transplantation. This principally happens in the first period after transplantation. Antibiotics and, most of all, immunosuppressive drugs are the main responsible. The relationship between immunosuppressive drugs and the gut microbiota is bilateral. From one side immunosuppressive drugs modify the gut microbiota, often generating dysbiosis; from the other side microbiota may interfere with the immunosuppressant pharmacokinetics, producing products more or less active with respect to the original drug. These phenomena have influence over the graft outcomes and clinical consequences as rejections, infections, diarrhea may be caused by the dysbiotic condition. Corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus and cyclosporine, mycophenolate mofetil and mTOR inhibitors are the immunosuppressive drugs whose effect on the gut microbiota is better known. In contrast is well known how the gut microbiota may interfere with glucocorticoids, which may be transformed into androgens. Tacrolimus may be transformed by micro biota into a product called M1 that is 15-fold less active with respect to tacrolimus. The pro-drug mycophenolate mofetil is normally transformed in mycophenolic acid that according the presence or not of microbes producing the enzyme glu curonidase, may be transformed into the inactive product.
Keywords: Dysbiosis; Graft outcomes; Gut microbiota; Immunosuppressive therapy; Kidney transplantation; Pathobionts.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Calcineurin inhibitor-free immunosuppression in pediatric renal transplantation: a viable option?Paediatr Drugs. 2011 Feb 1;13(1):49-69. doi: 10.2165/11538530-000000000-00000. Paediatr Drugs. 2011. PMID: 21162600 Review.
-
Immunosuppressive therapy after solid organ transplantation and the gut microbiota: Bidirectional interactions with clinical consequences.Am J Transplant. 2022 Apr;22(4):1014-1030. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16836. Epub 2021 Oct 15. Am J Transplant. 2022. PMID: 34510717 Review.
-
Influence of the new immunosuppressive combinations on arterial hypertension after renal transplantation.Kidney Int Suppl. 2002 Dec;(82):S81-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.62.s82.16.x. Kidney Int Suppl. 2002. PMID: 12410861 Review.
-
Microbiota, renal disease and renal transplantation.World J Transplant. 2021 Mar 18;11(3):16-36. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v11.i3.16. World J Transplant. 2021. PMID: 33816144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How cyclosporine reduces mycophenolic acid exposure by 40% while other calcineurin inhibitors do not.Kidney Int. 2021 Dec;100(6):1185-1189. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.06.036. Epub 2021 Jul 17. Kidney Int. 2021. PMID: 34284043 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunosuppressants Rewire the Gut Microbiome-Alloimmune Axis Through Time-Dependent and Tissue-Specific Mechanisms.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 11:2025.01.02.631100. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.02.631100. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40672154 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
A Case Series Report on the Effect of Tofacitinib on Joint Inflammation and Gut Microbiota Composition in Psoriatic Arthritis Patients Naive to Biologic Agents.Microorganisms. 2024 Nov 21;12(12):2387. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12122387. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39770590 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Microbiota in Patients Receiving Dialysis: A Review.Pathogens. 2024 Sep 15;13(9):801. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13090801. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39338992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the top 30 drugs associated with drug-induced constipation based on the FDA adverse event reporting system.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 2;15:1443555. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1443555. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39286628 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yu DH, Ying N, Lian ZH, Fa YQ. The Alteration human of gut microbiota and metabolites before and after renal transplantation. Microb Pathog. 2021;160:105191. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

