Thrombotic microangiopathy after kidney transplantation: Expanding etiologic and pathogenetic spectra
- PMID: 38576763
- PMCID: PMC10989473
- DOI: 10.5500/wjt.v14.i1.90277
Thrombotic microangiopathy after kidney transplantation: Expanding etiologic and pathogenetic spectra
Abstract
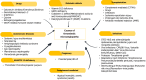
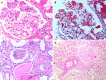
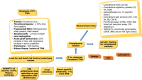
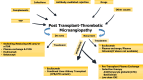
Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) is an uncommon but serious complication that not only affects native kidneys but also transplanted kidneys. This review is specifically focused on post-transplant TMA (PT-TMA) involving kidney transplant recipients. Its reported prevalence in the latter population varies from 0.8% to 14% with adverse impacts on both graft and patient survival. It has many causes and associations, and the list of etiologic agents and associations is growing constantly. The pathogenesis is equally varied and a variety of patho genetic pathways lead to the development of microvascular injury as the final common pathway. PT-TMA is categorized in many ways in order to facilitate its management. Ironically, more than one causes are contributory in PT-TMA and it is often difficult to pinpoint one particular cause in an individual case. Pathologically, the hallmark lesions are endothelial cell injury and intravascular thrombi affecting the microvasculature. Early diagnosis and classification of PT-TMA are imperative for optimal outcomes but are challenging for both clinicians and pathologists. The Banff classification has addressed this issue and has developed minimum diagnostic criteria for pathologic diagnosis of PT-TMA in the first phase. Management of the condition is also challenging and still largely empirical. It varies from simple maneuvers, such as plasmapheresis, drug withdrawal or modification, or dose reduction, to lifelong complement blockade, which is very expensive. A thorough understanding of the condition is imperative for an early diagnosis and quick treatment when the treatment is potentially effective. This review aims to increase the awareness of relevant stakeholders regarding this important, potentially treatable but under-recognized cause of kidney allograft dysfunction.
Keywords: Anemia; Kidney allograft failure; Microvascular injury; Thrombocytopenia; Thrombotic microangiopathy.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors have no conflict-of-interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Thrombotic microangiopathy after renal transplantation: Current insights in de novo and recurrent disease.World J Transplant. 2018 Sep 10;8(5):122-141. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v8.i5.122. World J Transplant. 2018. PMID: 30211021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
De novo thrombotic microangiopathy in two kidney transplant recipients from the same deceased donor: A case series.Clin Transplant. 2020 Jul;34(7):e13885. doi: 10.1111/ctr.13885. Epub 2020 May 27. Clin Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32314417
-
De novo thrombotic microangiopathy after kidney transplantation.Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2018 Jan;32(1):58-68. doi: 10.1016/j.trre.2017.10.001. Epub 2017 Nov 4. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2018. PMID: 29157988 Review.
-
De novo thrombotic microangiopathy after kidney transplantation: clinical features, treatment, and long-term patient and graft survival.Transplant Proc. 2012 Oct;44(8):2388-90. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2012.07.039. Transplant Proc. 2012. PMID: 23026601
-
Thrombotic Microangiopathy in the Renal Allograft: Results of the TMA Banff Working Group Consensus on Pathologic Diagnostic Criteria.Transpl Int. 2023 Aug 23;36:11590. doi: 10.3389/ti.2023.11590. eCollection 2023. Transpl Int. 2023. PMID: 37680648 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Thrombotic Microangiopathy After Kidney Pancreas Transplant Managed With Eculizumab and a Calcineurin Inhibitor-free Basiliximab/Belatacept Maintenance Regimen: Between a Rock and a Hard Place.Transplant Direct. 2025 Jun 12;11(7):e1825. doi: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000001825. eCollection 2025 Jul. Transplant Direct. 2025. PMID: 40519672 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Conservative Management of Thrombotic Microangiopathy in a Renal Transplant Recipient: The Importance of Early Recognition.Clin Case Rep. 2025 Mar 27;13(4):e70351. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.70351. eCollection 2025 Apr. Clin Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40151310 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

