Brain serotonin and serotonin transporter expression in male and female postnatal rat offspring in response to perturbed early life dietary exposures
- PMID: 38576870
- PMCID: PMC10991790
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1363094
Brain serotonin and serotonin transporter expression in male and female postnatal rat offspring in response to perturbed early life dietary exposures
Abstract
Introduction: Serotonin (5-HT) is critical for neurodevelopment and the serotonin transporter (SERT) modulates serotonin levels. Perturbed prenatal and postnatal dietary exposures affect the developing offspring predisposing to neurobehavioral disorders in the adult. We hypothesized that the postnatal brain 5-HT-SERT imbalance associated with gut dysbiosis forms the contributing gut-brain axis dependent mechanism responsible for such ultimate phenotypes.
Methods: Employing maternal diet restricted (IUGR, n=8) and high fat+high fructose (HFhf, n=6) dietary modifications, rodent brain serotonin was assessed temporally by ELISA and SERT by quantitative Western blot analysis. Simultaneously, colonic microbiome studies were performed.
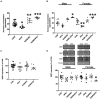
Results: At early postnatal (P) day 2 no changes in the IUGR, but a ~24% reduction in serotonin (p = 0.00005) in the HFhf group occurred, particularly in the males (p = 0.000007) revealing a male versus female difference (p = 0.006). No such changes in SERT concentrations emerged. At late P21 the IUGR group reared on HFhf (IUGR/HFhf, (n = 4) diet revealed increased serotonin by ~53% in males (p = 0.0001) and 36% in females (p = 0.023). While only females demonstrated a ~40% decrease in serotonin (p = 0.010), the males only trended lower without a significant change within the HFhf group (p = 0.146). SERT on the other hand was no different in HFhf or IUGR/RC, with only the female IUGR/HFhf revealing a 28% decrease (p = 0.036). In colonic microbiome studies, serotonin-producing Bacteriodes increased with decreased Lactobacillus at P2, while the serotonin-producing Streptococcus species increased in IUGR/HFhf at P21. Sex-specific changes emerged in association with brain serotonin or SERT in the case of Alistipase, Anaeroplasma, Blautia, Doria, Lactococcus, Proteus, and Roseburia genera.
Discussion: We conclude that an imbalanced 5-HT-SERT axis during postnatal brain development is sex-specific and induced by maternal dietary modifications related to postnatal gut dysbiosis. We speculate that these early changes albeit transient may permanently alter critical neural maturational processes affecting circuitry formation, thereby perturbing the neuropsychiatric equipoise.
Keywords: caloric restriction; high fat diet; intrauterine growth restriction; microbiome; serotonin; serotonin transporter.
Copyright © 2024 Ye, Ghosh, Shin, Ganguly, Maggiotto, Jacobs and Devaskar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Developing Brain Glucose Transporters, Serotonin, Serotonin Transporter, and Oxytocin Receptor Expression in Response to Early-Life Hypocaloric and Hypercaloric Dietary, and Air Pollutant Exposures.Dev Neurosci. 2021;43(1):27-42. doi: 10.1159/000514709. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Dev Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33774619 Free PMC article.
-
Variation in the Early Life and Adult Intestinal Microbiome of Intra-Uterine Growth Restricted Rat Offspring Exposed to a High Fat and Fructose Diet.Nutrients. 2023 Jan 1;15(1):217. doi: 10.3390/nu15010217. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36615874 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal fluoxetine treatment and dams' early life stress history alter affective behavior in rat offspring depending on serotonin transporter genotype and sex.Behav Brain Res. 2020 Aug 17;392:112657. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2020.112657. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Behav Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 32339551
-
Impact of diet on the persistence of early vascular remodeling and stiffening induced by intrauterine growth restriction and a maternal high-fat diet.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019 Aug 1;317(2):H424-H433. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00127.2019. Epub 2019 Jun 21. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31225985
-
Pathobiological and molecular connections involved in the high fructose and high fat diet induced diabetes associated nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Inflamm Res. 2020 Sep;69(9):851-867. doi: 10.1007/s00011-020-01373-7. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Inflamm Res. 2020. PMID: 32577775 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Serotonin Transporter Absence on Brain Insulin Receptor Expression, Plasma Metabolome Changes, and ADHD-like Behavior in Mice fed a Western Diet.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 23;14(8):884. doi: 10.3390/biom14080884. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39199273 Free PMC article.
-
Juvenile fluoxetine treatment affects the maturation of the medial prefrontal cortex and behavior of adolescent female rats.Pharmacol Rep. 2025 Jun;77(3):670-688. doi: 10.1007/s43440-025-00712-x. Epub 2025 Mar 10. Pharmacol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40063219
References
-
- Barandouzi Z. A., Lee J., Del Carmen Rosas M., Chen J., Henderson W. A., Starkweather A. R., et al. . (2022). Associations of neurotransmitters and the gut microbiome with emotional distress in mixed type of irritable bowel syndrome. Sci. Rep. 12:1648. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05756-0, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

