"Crosstalk between non-coding RNAs and transcription factor LRF in non-small cell lung cancer"
- PMID: 38577020
- PMCID: PMC10990748
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.03.009
"Crosstalk between non-coding RNAs and transcription factor LRF in non-small cell lung cancer"
Abstract
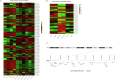
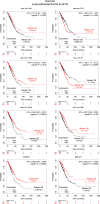
Epigenetic approaches in direct correlation with assessment of critical genetic mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) are currently very intensive, as the epigenetic components underlying NSCLC development and progression have attained high recognition. In this level of research, established human NSCLC cell lines as well as experimental animals are widely used to detect novel biomarkers and pharmacological targets to treat NSCLC. The epigenetic background holds a great potential for the identification of epi-biomarkers for treatment response however, it is highly complex and requires precise definition as these phenomena are variable between NSCLC subtypes and systems origin. We engaged an in-depth characterization of non-coding (nc)RNAs prevalent in human KRAS-mutant NSCLC cell lines A549 and H460 and mouse KRAS-mutant NSCLC tissue by Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) and quantitative Real Time PCRs (qPCRs). Also, the transcription factor (TF) LRF, a known epigenetic silencer, was examined as a modulator of non-coding RNAs expression. Finally, interacting networks underlying epigenetic variations in NSCLC subtypes were created. Data derived from our study highlights the divergent epigenetic profiles of NSCLC of human and mouse origin, as well as the significant contribution of 12qf1: 109,709,060-109,747,960 mouse chromosomal region to micro-RNA upregulated species. Furthermore, the novel epigenetic miR-148b-3p/lncPVT1/ZBTB7A axis was identified, which differentiates human cell line of lung adenocarcinoma from large cell lung carcinoma, two characteristic NSCLC subtypes. The detailed recording of epigenetic events in NSCLC and combinational studies including networking between ncRNAs and TFs validate the identification of significant epigenetic features, prevailing in NSCLC subtypes and among experimental models. Our results enrich knowledge in the field and empower research on the epigenetic prognostic biomarkers of the disease progression, NSCLC subtypes discrimination and advancement to patient-tailored treatments.
Keywords: Epigenetic deregulation; Epigenetic networks; Long non-coding RNAs; Micro-RNAs; Non-small cell lung cancer; Transcription factor LRF.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Ifigeneia Makariti is financially supported by BioAnalytica SA, Biotechnology supplier company and also a member of the research team of biology HOU lab. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Characterization and selective incorporation of small non-coding RNAs in non-small cell lung cancer extracellular vesicles.Cell Biosci. 2018 Jan 10;8:2. doi: 10.1186/s13578-018-0202-x. eCollection 2018. Cell Biosci. 2018. PMID: 29344346 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA as potential biomarkers in non-small-cell lung cancer: What do we know so far?Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 May;101:322-333. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.099. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29499406 Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA NORAD promotes the occurrence and development of non-small cell lung cancer by adsorbing MiR-656-3p.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019 Aug;7(8):e757. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.757. Epub 2019 Jun 17. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019. Retraction in: Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2023 Jan;11(1):e2112. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.2112. PMID: 31207175 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Circular RNA_0120376 regulates microRNA-148b-3 and centrosomal protein 55 to promote non-small cell lung cancer development.Bioengineered. 2022 May;13(5):11844-11855. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2052647. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35549631 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the interplay between methylation patterns and non-coding RNAs in non-small cell lung cancer: Implications for pathogenesis and therapeutic targets.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 19;10(2):e24811. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24811. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38312618 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Repression of ZNFX1 by LncRNA ZFAS1 mediates tobacco-induced pulmonary carcinogenesis.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Apr 10;30(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00705-x. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40211119 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA MEG3/CTCF-CXCR4 axis functions in the regulation of breast cancer cell migration.Noncoding RNA Res. 2025 May 28;14:117-128. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2025.05.014. eCollection 2025 Oct. Noncoding RNA Res. 2025. PMID: 40548301 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Travis W.D., et al. The 2015 world health organization classification of lung tumors: impact of genetic, clinical and radiologic advances since the 2004 classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015;10(9):1243–1260. - PubMed
-
- Horie M., et al. Integrative CAGE and DNA methylation profiling identify epigenetically regulated genes in NSCLC. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017;15(10):1354–1365. - PubMed
-
- Chang A. Chemotherapy, chemoresistance and the changing treatment landscape for NSCLC. Lung Cancer. 2011;71(1):3–10. - PubMed
-
- Jones P.A., Baylin S.B. The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002;3(6):415–428. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

