Pre-operative visceral adipose tissue radiodensity is a potentially novel prognostic biomarker for early endoscopic post-operative recurrence in Crohn's disease
- PMID: 38577075
- PMCID: PMC10989343
- DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i3.740
Pre-operative visceral adipose tissue radiodensity is a potentially novel prognostic biomarker for early endoscopic post-operative recurrence in Crohn's disease
Abstract
Background: Evidence suggests inflammatory mesenteric fat is involved in post-operative recurrence (POR) of Crohn's disease (CD). However, its prognostic value is uncertain, in part, due to difficulties studying it non-invasively.
Aim: To evaluate the prognostic value of pre-operative radiographic mesenteric parameters for early endoscopic POR (ePOR).
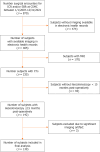
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study of CD subjects ≥ 12 years who underwent ileocecal or small bowel resection between 1/1/2007 to 12/31/2021 with computerized tomography abdomen/pelvis ≤ 6 months pre-operatively and underwent ileocolonoscopy ≤ 15 months post-operatively. Visceral adipose tissue (VAT) volume (cm3), ratio of VAT:subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) volume, VAT radiodensity, and ratio of VAT:SAT radiodensity were generated semiautomatically. Mesenteric lymphadenopathy (LAD, largest lymph node > 10 mm) and severe vasa recta (VR) engorgement (diameter of the VR supplying diseased bowel ≥ 2 × VR supplying healthy bowel) were derived manually. The primary outcome was early ePOR (Rutgeert's score ≥ i2 on first endoscopy ≤ 15 months post-operatively) and the secondary outcome was ePOR severity (Rutgeert's score i0-4). Regression analyses were performed adjusting for demographic and disease-related characteristics to calculate adjusted odds ratio (aOR) and 95% confidence interval (CI).
Results: Of the 139 subjects included, 45% of subjects developed early ePOR (n = 63). VAT radiodensity (aOR 0.59, 95%CI: 0.38-0.90) and VAT:SAT radiodensity (aOR 8.54, 95%CI: 1.48-49.28) were associated with early ePOR, whereas, VAT volume (aOR 1.23, 95%CI: 0.78-1.95), VAT:SAT volume (aOR 0.80, 95%CI: 0.53-1.20), severe VR engorgement (aOR 1.53, 95%CI: 0.64-3.66), and mesenteric LAD (aOR 1.59, 95%CI: 0.67-3.79) were not. Similar results were observed for severity of ePOR.
Conclusion: VAT radiodensity is potentially a novel non-invasive prognostic imaging marker to help risk stratify CD patients for POR.
Keywords: Computed tomography; Creeping fat; Crohn’s disease; Mesenteric adipose tissue; Surgery; Visceral adipose tissue.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Li D has received consulting fees from Prometheus Biosciences Inc; Syal G has received research support from Pfizer; Yarur AJ has received consulting fees from Bristol Myers Squibb, Arena, Pfizer, Takeda and Landos; Targan SR serves on the scientific advisory board for Seaver Foundation for Austim, and has stock options in Promethus Biosciences Inc; Ziring D is on the speaking bureau for AbbVie, Prometheus Labs, and Regeneron; Rabizadeh S has advised for Prometheus and Janssen; Melmed GY has received consulting fees from Abbvie, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, Dieta, Entasis, Fresenius Kabi, Genentech, Gilead, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, Oshi, Prometheus Labs, Pfizer, Takeda, Techlab; Fleshner P has received consulting fees from Takeda; McGovern DPB has received consulting fees from Takeda, Prometheus Biosciences Inc, Prometheus Labs; Other authors have no conflicts of interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Visceral adiposity and inflammatory bowel disease.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021 Nov;36(11):2305-2319. doi: 10.1007/s00384-021-03968-w. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021. PMID: 34104989 Review.
-
CT-based radiomics signature of visceral adipose tissue for prediction of disease progression in patients with Crohn's disease: A multicentre cohort study.EClinicalMedicine. 2022 Dec 30;56:101805. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101805. eCollection 2023 Feb. EClinicalMedicine. 2022. PMID: 36618894 Free PMC article.
-
Visceral Adipose Tissue Volumetrics Inform Odds of Treatment Response and Risk of Subsequent Surgery in IBD Patients Starting Antitumor Necrosis Factor Therapy.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2022 May 4;28(5):657-666. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izab167. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2022. PMID: 34291800
-
Comparative Persistence of Non-tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) vs. TNF Antagonists for Post-operative Prophylaxis in Crohn's Disease (CD).Dig Dis Sci. 2024 Jan;69(1):235-245. doi: 10.1007/s10620-023-08192-w. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Dig Dis Sci. 2024. PMID: 38015321 Free PMC article.
-
Adipose tissue density on CT as a prognostic factor in patients with cancer: a systematic review.Acta Oncol. 2020 Dec;59(12):1488-1495. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2020.1800087. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Acta Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32730106
References
-
- Ng SC, Shi HY, Hamidi N, Underwood FE, Tang W, Benchimol EI, Panaccione R, Ghosh S, Wu JCY, Chan FKL, Sung JJY, Kaplan GG. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet. 2017;390:2769–2778. - PubMed
-
- Tsai L, Ma C, Dulai PS, Prokop LJ, Eisenstein S, Ramamoorthy SL, Feagan BG, Jairath V, Sandborn WJ, Singh S. Contemporary Risk of Surgery in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn's Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Population-Based Cohorts. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19:2031–2045.e11. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stevens TW, Haasnoot ML, D'Haens GR, Buskens CJ, de Groof EJ, Eshuis EJ, Gardenbroek TJ, Mol B, Stokkers PCF, Bemelman WA, Ponsioen CY LIR!C study group. Laparoscopic ileocaecal resection vs infliximab for terminal ileitis in Crohn's disease: retrospective long-term follow-up of the LIR!C trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5:900–907. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials