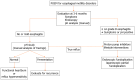
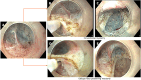
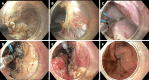
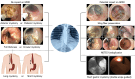
Prediction, prevention and management of gastroesophageal reflux after per-oral endoscopic myotomy: An update
- PMID: 38577183
- PMCID: PMC10989487
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1096
Prediction, prevention and management of gastroesophageal reflux after per-oral endoscopic myotomy: An update
Abstract
Achalasia cardia, the most prevalent primary esophageal motility disorder, is predominantly characterized by symptoms of dysphagia and regurgitation. The principal therapeutic approaches for achalasia encompass pneumatic dilatation (PD), Heller's myotomy, and the more recent per-oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM). POEM has been substantiated as a safe and efficacious modality for the management of achalasia. Although POEM demonstrates superior efficacy compared to PD and an efficacy parallel to Heller's myotomy, the incidence of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) following POEM is notably higher than with the aforementioned techniques. While symptomatic reflux post-POEM is relatively infrequent, the significant occurrence of erosive esophagitis and heightened esophageal acid exposure necessitates vigilant monitoring to preclude long-term GERD-related complications. Contemporary advancements in the field have enhanced our comprehension of the risk factors, diagnostic methodologies, preventative strategies, and therapeutic management of GERD subsequent to POEM. This review focuses on the limitations inherent in the 24-h pH study for evaluating post-POEM reflux, potential modifications in the POEM technique to mitigate GERD risk, and the strategies for managing reflux following POEM.
Keywords: Achalasia cardia; Esophagitis; Gastroesophageal reflux; Gastroesophageal reflux disease; Per-oral endoscopic myotomy.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Authors declare no conflict of interests for this article.
Figures

References
-
- Jung HK, Hong SJ, Lee OY, Pandolfino J, Park H, Miwa H, Ghoshal UC, Mahadeva S, Oshima T, Chen M, Chua ASB, Cho YK, Lee TH, Min YW, Park CH, Kwon JG, Park MI, Jung K, Park JK, Jung KW, Lim HC, Jung DH, Kim DH, Lim CH, Moon HS, Park JH, Choi SC, Suzuki H, Patcharatrakul T, Wu JCY, Lee KJ, Tanaka S, Siah KTH, Park KS, Kim SE Korean Society of Neurogastroenterology and Motility. 2019 Seoul Consensus on Esophageal Achalasia Guidelines. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2020;26:180–203. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Khashab MA, Vela MF, Thosani N, Agrawal D, Buxbaum JL, Abbas Fehmi SM, Fishman DS, Gurudu SR, Jamil LH, Jue TL, Kannadath BS, Law JK, Lee JK, Naveed M, Qumseya BJ, Sawhney MS, Yang J, Wani S. ASGE guideline on the management of achalasia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91:213–227.e6. - PubMed
-
- Oude Nijhuis RAB, Zaninotto G, Roman S, Boeckxstaens GE, Fockens P, Langendam MW, Plumb AA, Smout A, Targarona EM, Trukhmanov AS, Weusten B, Bredenoord AJ. European guidelines on achalasia: United European Gastroenterology and European Society of Neurogastroenterology and Motility recommendations. United European Gastroenterol J. 2020;8:13–33. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nabi Z, Ramchandani M, Reddy DN. Per-oral endoscopic myotomy and gastroesophageal reflux: Where do we stand after a decade of "POETRY"? Indian J Gastroenterol. 2019;38:287–294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

