Telomerase-related advances in hepatocellular carcinoma: A bibliometric and visual analysis
- PMID: 38577190
- PMCID: PMC10989492
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1224
Telomerase-related advances in hepatocellular carcinoma: A bibliometric and visual analysis
Abstract
Background: As a critical early event in hepatocellular carcinogenesis, telomerase activation might be a promising and critical biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients, and its function in the genesis and treatment of HCC has gained much attention over the past two decades.
Aim: To perform a bibliometric analysis to systematically assess the current state of research on HCC-related telomerase.
Methods: The Web of Science Core Collection and PubMed were systematically searched to retrieve publications pertaining to HCC/telomerase limited to "articles" and "reviews" published in English. A total of 873 relevant publications related to HCC and telomerase were identified. We employed the Bibliometrix package in R to extract and analyze the fundamental information of the publications, such as the trends in the publications, citation counts, most prolific or influential writers, and most popular journals; to screen for keywords occurring at high frequency; and to draw collaboration and cluster analysis charts on the basis of coauthorship and co-occurrences. VOSviewer was utilized to compile and visualize the bibliometric data.
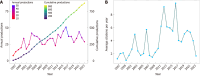
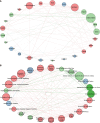
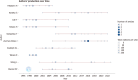
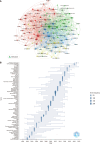
Results: A surge of 51 publications on HCC/telomerase research occurred in 2016, the most productive year from 1996 to 2023, accompanied by the peak citation count recorded in 2016. Up to December 2023, 35226 citations were made to all publications, an average of 46.6 citations to each paper. The United States received the most citations (n = 13531), followed by China (n = 7427) and Japan (n = 5754). In terms of national cooperation, China presented the highest centrality, its strongest bonds being to the United States and Japan. Among the 20 academic institutions with the most publications, ten came from China and the rest of Asia, though the University of Paris Cité, Public Assistance-Hospitals of Paris, and the National Institute of Health and Medical Research (INSERM) were the most prolific. As for individual contributions, Hisatomi H, Kaneko S, and Ide T were the three most prolific authors. Kaneko S ranked first by H-index, G-index, and overall publication count, while Zucman-Rossi J ranked first in citation count. The five most popular journals were the World Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Journal of Hepatology, Oncotarget, and Oncogene, while Nature Genetics, Hepatology, and Nature Reviews Disease Primers had the most citations. We extracted 2293 keywords from the publications, 120 of which appeared more than ten times. The most frequent were HCC, telomerase and human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT). Keywords such as mutational landscape, TERT promoter mutations, landscape, risk, and prognosis were among the most common issues in this field in the last three years and may be topics for research in the coming years.
Conclusion: Our bibliometric analysis provides a comprehensive overview of HCC/telomerase research and insights into promising upcoming research.
Keywords: Bibliometric analysis; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Prognosis; Telomerase; Telomerase reverse transcriptase; Treatment.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bibliometric study of immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 4;14:1210802. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1210802. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37600802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
Research landscape and frontiers of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-associated hepatocellular carcinoma: a bibliometric and visual analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 12;14:1240649. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1240649. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37771721 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge Mapping of Immunotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Bibliometric Study.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 31;13:815575. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.815575. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35173728 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of endoplasmic reticulum stress in hepatocellular carcinoma: trends and future directions.Discov Oncol. 2024 Sep 27;15(1):481. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01377-3. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39331256 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Global status and trends of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: A bibliometric study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 May 30;104(22):e42603. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042603. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40441187 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the evolution of liver aging research: A bibliometric analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Nov 7;30(41):4461-4480. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i41.4461. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39534417 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Villanueva A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1450–1462. - PubMed
-
- Mazzanti R, Gramantieri L, Bolondi L. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and clinical aspects. Mol Aspects Med. 2008;29:130–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

