Biogenic Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles synthesized from Tinospora Cordifolia induce oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage and apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 38577319
- PMCID: PMC10988208
- DOI: 10.7150/ntno.84995
Biogenic Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles synthesized from Tinospora Cordifolia induce oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage and apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
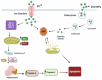
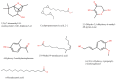
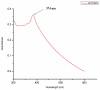
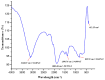
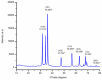
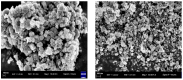
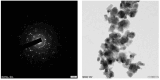
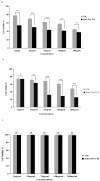
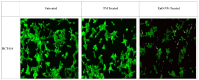
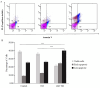
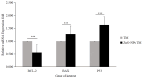
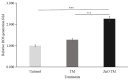
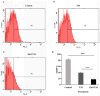
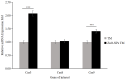
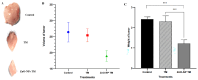
Cancer chemotherapy remains a serious challenge, and new approaches to therapy are urgently needed to build novel treatment regimens. The methanol extract of the stem of Tinospora Cordifolia was used to synthesize biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) that display anticancer activities against colorectal cancer. Biogenic ZnO-NPs synthesized from methanol extract of Tinospora Cordifolia stem (ZnO-NPs TM) were tested against HCT-116 cell lines to assess anticancer activity. UV-Vis, FTIR, XRD, SEM, and TEM analysis characterized the biogenic ZnO-NPs. To see how well biogenic ZnO-NPs fight cancer, cytotoxicity, AO/EtBr staining, Annexin V/PI staining, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) analysis, and caspase cascade activity analysis were performed to assess the anticancer efficacy of biogenic ZnO-NPs. The IC50 values of biogenic ZnO-NPs treated cells (HCT-116 and Caco-2) were 31.419 ± 0.682μg/ml and 36.675 ± 0.916μg/ml, respectively. qRT-PCR analysis showed that cells treated with biogenic ZnO-NPs Bax and P53 mRNA levels increased significantly (p ≤ 0.001). It showed to have impaired MMP and increased ROS generation. In a corollary, our in vivo study showed that biogenic ZnO-NPs have an anti-tumour effect. Biogenic ZnO-NPs TM showed both in vitro and in vivo anticancer effects that could be employed as anticancer drugs.
Keywords: Anticancer; Apoptosis; Caspase cascade; Colorectal cancer; Cytotoxicity; Green synthesis; MMP; ROS; biogenic ZnO-NPs; in vivo.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigating the Effects of Biogenic Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Produced Using Papaver somniferum Extract on Oxidative Stress, Cytotoxicity, and the Induction of Apoptosis in the THP-1 Cell Line.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023 Oct;201(10):4697-4709. doi: 10.1007/s12011-023-03574-7. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023. PMID: 36662347
-
Zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized from Aspergillus terreus induces oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis through modulating apoptotic proteins in human cervical cancer HeLa cells.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 4;73(2):221-232. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgaa043. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33793807
-
In vitro localization of modified zinc oxide nanoparticles showing selective anticancer effects against colorectal carcinoma using biophysical techniques.Sci Rep. 2025 May 14;15(1):16811. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00434-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40369004 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles and zinc oxide nanoparticles to human epithelial colorectal adenocarcinoma (Caco-2) cells.Mutat Res. 2014 Nov;769:113-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2014.08.001. Epub 2014 Aug 12. Mutat Res. 2014. PMID: 25771730
-
Cutting-edge nanotechnology: unveiling the role of zinc oxide nanoparticles in combating deadly gastrointestinal tumors.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Mar 20;13:1547757. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1547757. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40182988 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the potency of ZnO and CuO nanocomposites in combating hepatocellular carcinoma by inducing cell death and suppressing migration.Sci Rep. 2025 May 3;15(1):15477. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97395-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40319186 Free PMC article.
-
Tailoring CdO-CuO-ZnO Mixed Metal Oxide Nanocomposites for Anticancer Activity via Co-Precipitation Method.Nanotechnol Sci Appl. 2025 May 7;18:225-244. doi: 10.2147/NSA.S519229. eCollection 2025. Nanotechnol Sci Appl. 2025. PMID: 40357522 Free PMC article.
-
Sustainable synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Persicaria lapathifolia: versatile anticancer and antibacterial applications.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Jul 7;12:1601811. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1601811. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40692720 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Zinc Oxide-Doped Carbon Dots for Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Dec 27;19:13949-13971. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S494262. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39742095 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in nanotechnology for colorectal cancer: a smart targeting and theranostics approach.Med Oncol. 2025 Jul 18;42(8):346. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02910-2. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40679715 Review.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I. et al. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. International journal of cancer. 2019;144(8):1941–53. - PubMed
-
- Verma SK, Panda PK, Kumari P. et al. Determining factors for the nano-biocompatibility of cobalt oxide nanoparticles: proximal discrepancy in intrinsic atomic interactions at differential vicinage. Green Chemistry. 2021;23(9):3439–58.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

