Biogenic Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles synthesized from Tinospora Cordifolia induce oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage and apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 38577319
- PMCID: PMC10988208
- DOI: 10.7150/ntno.84995
Biogenic Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles synthesized from Tinospora Cordifolia induce oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage and apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
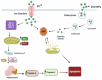
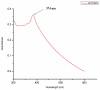
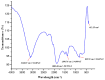
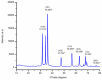
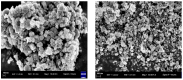
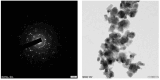
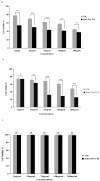
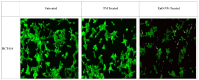
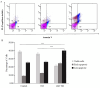
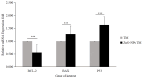
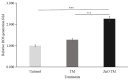
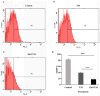
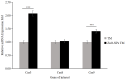
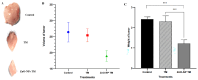
Cancer chemotherapy remains a serious challenge, and new approaches to therapy are urgently needed to build novel treatment regimens. The methanol extract of the stem of Tinospora Cordifolia was used to synthesize biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) that display anticancer activities against colorectal cancer. Biogenic ZnO-NPs synthesized from methanol extract of Tinospora Cordifolia stem (ZnO-NPs TM) were tested against HCT-116 cell lines to assess anticancer activity. UV-Vis, FTIR, XRD, SEM, and TEM analysis characterized the biogenic ZnO-NPs. To see how well biogenic ZnO-NPs fight cancer, cytotoxicity, AO/EtBr staining, Annexin V/PI staining, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) analysis, and caspase cascade activity analysis were performed to assess the anticancer efficacy of biogenic ZnO-NPs. The IC50 values of biogenic ZnO-NPs treated cells (HCT-116 and Caco-2) were 31.419 ± 0.682μg/ml and 36.675 ± 0.916μg/ml, respectively. qRT-PCR analysis showed that cells treated with biogenic ZnO-NPs Bax and P53 mRNA levels increased significantly (p ≤ 0.001). It showed to have impaired MMP and increased ROS generation. In a corollary, our in vivo study showed that biogenic ZnO-NPs have an anti-tumour effect. Biogenic ZnO-NPs TM showed both in vitro and in vivo anticancer effects that could be employed as anticancer drugs.
Keywords: Anticancer; Apoptosis; Caspase cascade; Colorectal cancer; Cytotoxicity; Green synthesis; MMP; ROS; biogenic ZnO-NPs; in vivo.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I. et al. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. International journal of cancer. 2019;144(8):1941–53. - PubMed
-
- Verma SK, Panda PK, Kumari P. et al. Determining factors for the nano-biocompatibility of cobalt oxide nanoparticles: proximal discrepancy in intrinsic atomic interactions at differential vicinage. Green Chemistry. 2021;23(9):3439–58.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

