Sepsis, Management & Advances in Metabolomics
- PMID: 38577320
- PMCID: PMC10988213
- DOI: 10.7150/ntno.94071
Sepsis, Management & Advances in Metabolomics
Abstract
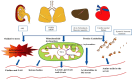
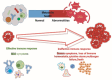
Though there have been developments in clinical care and management, early and accurate diagnosis and risk stratification are still bottlenecks in septic shock patients. Since septic shock is multifactorial with patient-specific underlying co-morbid conditions, early assessment of sepsis becomes challenging due to variable symptoms and clinical manifestations. Moreover, the treatment strategies are traditionally based on their progression and corresponding clinical symptoms, not personalized. The complex pathophysiology assures that a single biomarker cannot identify, stratify, and describe patients affected by septic shock. Traditional biomarkers like CRP, PCT, and cytokines are not sensitive and specific enough to be used entirely for a patient's diagnosis and prognosis. Thus, the need of the hour is a sensitive and specific biomarker after comprehensive analysis that may facilitate an early diagnosis, prognosis, and drug development. Integration of clinical data with metabolomics would provide means to understand the patient's condition, stratify patients better, and predict the clinical outcome.
Keywords: biomarker; critical care; metabolomics; sepsis; septic shock.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

