Adipose-derived stem cell exosomes act as delivery vehicles of microRNAs in a dog model of chronic hepatitis
- PMID: 38577321
- PMCID: PMC10988209
- DOI: 10.7150/ntno.93064
Adipose-derived stem cell exosomes act as delivery vehicles of microRNAs in a dog model of chronic hepatitis
Abstract
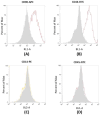
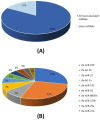
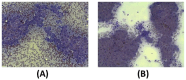
Exosomes are nanosized extracellular vesicles secreted by all cell types, including canine adipose-derived stem cells (cADSCs). By mediating intercellular communication, exosomes modulate the biology of adjacent and distant cells by transferring their cargo. In the present work after isolation and characterization of exosomes derived from canine adipose tissue, we treated the same canine donors affected by hepatopathies with the previously isolated exosomes. We hypothesize that cADSC-sourced miRNAs are among the factors responsible for a regenerative and anti-inflammatory effect in the treatment of hepatopathies in dogs, providing the clinical veterinary field with an effective and innovative cell-free therapy. Exosomes were isolated and characterized for size, distribution, surface markers, and for their miRNomic cargo by microRNA sequencing. 295 dogs affected with hepatopathies were treated and followed up for 6 months to keep track of their biochemical marker levels. Results confirmed that exosomes derived from cADSCs exhibited an average diameter of 91 nm, and positivity to 8 known exosome markers. The administration of exosomes to dogs affected by liver-associated inflammatory pathologies resulted in the recovery of the animal alongside the normalization of biochemical parameters of kidney function. In conclusion, cADSCs-derived exosomes are a promising therapeutic tool for treating inflammatory disorders in animal companions.
Keywords: exosomes; extracellular nanovesicles; liver diseases; miRNA; regenerative medicine..
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

