circular RNA circ-231 promotes protein biogenesis of TPI1 and PRDX6 through mediating the interaction of eIF4A3 with STAU1 to facilitate unwinding of secondary structure in 5' UTR, enhancing progression of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC)
- PMID: 38577609
- PMCID: PMC10988296
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.92578
circular RNA circ-231 promotes protein biogenesis of TPI1 and PRDX6 through mediating the interaction of eIF4A3 with STAU1 to facilitate unwinding of secondary structure in 5' UTR, enhancing progression of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC)
Abstract
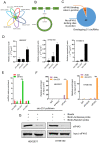
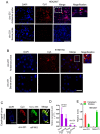
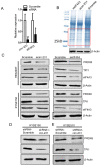
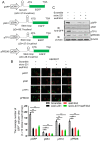
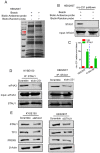
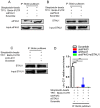
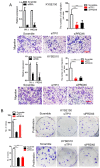
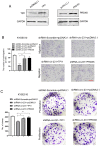
Background: The nuclear cap-binding complex (CBC)-dependent translation (CT) is an important initial translation pathway for 5'-cap-dependent translation in normal mammal cells. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A-III (eIF4A3), as an RNA helicase, is recruited to CT complex and enhances CT efficiency through participating in unwinding of secondary structure in the 5' UTR. However, the detailed mechanism for eIF4A3 implicated in unwinding of secondary structure in the 5' UTR in normal mammal cells is still unclear. Specially, we need to investigate whether the kind of mechanism in normal mammal cells extrapolates to cancer cells, e.g. ESCC, and further interrogate whether and how the mechanism triggers malignant phenotype of ESCC, which are important for identifying a potential therapeutic target for patients with ESCC. Methods: Bioinformatics analysis, RNA immunoprecipitation and RNA pulldown assays were performed to detect the interaction of circular RNA circ-231 with eIF4A3. In vitro and in vivo assays were performed to detect biological roles of circ-231 in ESCC. RNA immunoprecipitation, RNA pulldown, mass spectrometry analysis and co-immunoprecipitation assays were used to measure the interaction of circ-231, eIF4A3 and STAU1 in HEK293T and ESCC. In vitro EGFP reporter and 5' UTR of mRNA pulldown assays were performed to probe for the binding of circ-231, eIF4A3 and STAU1 to secondary structure of 5' UTR. Results: RNA immunoprecipitation assays showed that circ-231 interacted with eIF4A3 in HEK293T and ESCC. Further study confirmed that circ-231 orchestrated with eIF4A3 to control protein expression of TPI1 and PRDX6, but not for mRNA transcripts. The in-depth mechanism study uncovered that both circ-231 and eIF4A3 were involved in unwinding of secondary structure in 5' UTR of TPI1 and PRDX6. More importantly, circ-231 promoted the interaction between eIF4A3 and STAU1. Intriguingly, both circ-231 and eIF4A3 were dependent on STAU1 binding to secondary structure in 5' UTR. Biological function assays revealed that circ-231 promoted the migration and proliferation of ESCC via TPI1 and PRDX6. In ESCC, the up-regulated expression of circ-231 was observed and patients with ESCC characterized by higher expression of circ-231 have concurrent lymph node metastasis, compared with control. Conclusions: Our data unravels the detailed mechanism by which STAU1 binds to secondary structure in 5' UTR of mRNAs and recruits eIF4A3 through interacting with circ-231 and thereby eIF4A3 is implicated in unwinding of secondary structure, which is common to HEK293T and ESCC. However, importantly, our data reveals that circ-231 promotes migration and proliferation of ESCC and the up-regulated circ-231 greatly correlates with tumor lymph node metastasis, insinuating that circ-231 could be a therapeutic target and an indicator of risk of lymph node metastasis for patients with ESCC.
Keywords: Interaction; RNA binding protein; STAU1; circ-231; eIF4A3.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

