Post-transcriptional splicing can occur in a slow-moving zone around the gene
- PMID: 38577979
- PMCID: PMC10997330
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.91357
Post-transcriptional splicing can occur in a slow-moving zone around the gene
Abstract
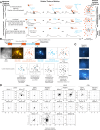
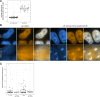
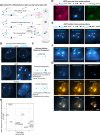
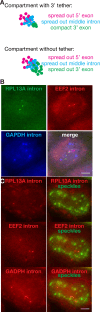
Splicing is the stepwise molecular process by which introns are removed from pre-mRNA and exons are joined together to form mature mRNA sequences. The ordering and spatial distribution of these steps remain controversial, with opposing models suggesting splicing occurs either during or after transcription. We used single-molecule RNA FISH, expansion microscopy, and live-cell imaging to reveal the spatiotemporal distribution of nascent transcripts in mammalian cells. At super-resolution levels, we found that pre-mRNA formed clouds around the transcription site. These clouds indicate the existence of a transcription-site-proximal zone through which RNA move more slowly than in the nucleoplasm. Full-length pre-mRNA undergo continuous splicing as they move through this zone following transcription, suggesting a model in which splicing can occur post-transcriptionally but still within the proximity of the transcription site, thus seeming co-transcriptional by most assays. These results may unify conflicting reports of co-transcriptional versus post-transcriptional splicing.
Keywords: chromosomes; expansion microscopy; gene expression; human; live-cell imaging; splicing.
© 2023, Coté, O'Farrell et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AC, AO, ID, MD, CC, YW, SB, HD, KA, FC, AW, RP, KP, EB, SB, JP, LC, AR No competing interests declared
Figures








Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2020.04.06.028092
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.91357.1
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.91357.2
References
-
- Aebi M, Weissman C. Precision and orderliness in splicing. Trends in Genetics. 1987;3:102–107. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(87)90193-4. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Dryad/10.5061/dryad.m0cfxppb7
Grants and funding
- R01 GM137425/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA238237/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 3R01CA078831-20S1/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA232256/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA174523/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21-HG009264/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA221010/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA238237/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA227550/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5F32CA221010-02/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA261608/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F31-GM122133/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- F31 GM122133/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007229/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-GM117333/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA232256/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK127405/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA227550/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- RM1 HG007743/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM137425/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL129998/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK127405/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM117333/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HG009264/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL129998/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016520/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA078831/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM-07229/NH/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

