Safety and Preliminary Efficacy of Pembrolizumab Following Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The PETAL Phase Ib Study
- PMID: 38578610
- PMCID: PMC11145164
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-0177
Safety and Preliminary Efficacy of Pembrolizumab Following Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The PETAL Phase Ib Study
Abstract
Purpose: Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) may prime adaptive immunity and enhance immunotherapy efficacy. PETAL evaluated safety, preliminary activity of TACE plus pembrolizumab and explored mechanisms of efficacy.
Patients and methods: Patients with liver-confined hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) were planned to receive up to two rounds of TACE followed by pembrolizumab 200 mg every 21 days commencing 30 days post-TACE until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity for up to 1 year. Primary endpoint was safety, with assessment window of 21 days from pembrolizumab initiation. Secondary endpoints included progression-free survival (PFS) and evaluation of tumor and host determinants of response.
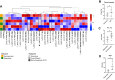
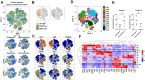
Results: Fifteen patients were included in the safety and efficacy population: 73% had nonviral cirrhosis; median age was 72 years. Child-Pugh class was A in 14 patients. Median tumor size was 4 cm. Ten patients (67%) received pembrolizumab after one TACE; 5 patients after two (33%). Pembrolizumab yielded no synergistic toxicity nor dose-limiting toxicities post-TACE. Treatment-related adverse events occurred in 93% of patients, most commonly skin rash (40%), fatigue, and diarrhea (27%). After a median follow-up of 38.5 months, objective response rate 12 weeks post-TACE was 53%. PFS rate at 12 weeks was 93% and median PFS was 8.95 months [95% confidence interval (CI): 7.30-NE (not estimable)]. Median duration of response was 7.3 months (95% CI: 6.3-8.3). Median overall survival was 33.5 months (95% CI: 11.6-NE). Dynamic changes in peripheral T-cell subsets, circulating tumor DNA, serum metabolites, and in stool bacterial profiles highlight potential mechanisms of action of multimodal therapy.
Conclusions: TACE plus pembrolizumab was tolerable with no evidence of synergistic toxicity, encouraging further clinical development of immunotherapy alongside TACE.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures


Comment in
-
Efficacy and challenges of combining transarterial chemoembolization with pembrolizumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: insights from the PETAL study.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2025 Apr 1;14(2):301-304. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-2025-36. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40342779 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Raoul JL, Forner A, Bolondi L, Cheung TT, Kloeckner R, de Baere T. Updated use of TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: how and when to use it based on clinical evidence. Cancer Treat Rev 2019;72:28–36. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Bruix J. Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology 2003;37:429–42. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Real MI, Montana X, Planas R, Coll S, Aponte J, et al. . Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2002;359:1734–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

