Single-cell 'omic profiles of human aortic endothelial cells in vitro and human atherosclerotic lesions ex vivo reveal heterogeneity of endothelial subtype and response to activating perturbations
- PMID: 38578680
- PMCID: PMC10997331
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.91729
Single-cell 'omic profiles of human aortic endothelial cells in vitro and human atherosclerotic lesions ex vivo reveal heterogeneity of endothelial subtype and response to activating perturbations
Abstract
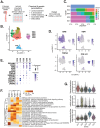
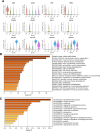
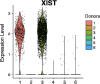
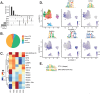
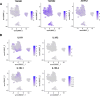
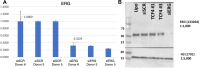
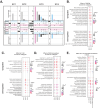
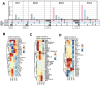
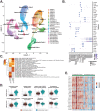
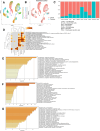
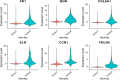
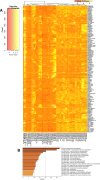
Heterogeneity in endothelial cell (EC) sub-phenotypes is becoming increasingly appreciated in atherosclerosis progression. Still, studies quantifying EC heterogeneity across whole transcriptomes and epigenomes in both in vitro and in vivo models are lacking. Multiomic profiling concurrently measuring transcriptomes and accessible chromatin in the same single cells was performed on six distinct primary cultures of human aortic ECs (HAECs) exposed to activating environments characteristic of the atherosclerotic microenvironment in vitro. Meta-analysis of single-cell transcriptomes across 17 human ex vivo arterial specimens was performed and two computational approaches quantitatively evaluated the similarity in molecular profiles between heterogeneous in vitro and ex vivo cell profiles. HAEC cultures were reproducibly populated by four major clusters with distinct pathway enrichment profiles and modest heterogeneous responses: EC1-angiogenic, EC2-proliferative, EC3-activated/mesenchymal-like, and EC4-mesenchymal. Quantitative comparisons between in vitro and ex vivo transcriptomes confirmed EC1 and EC2 as most canonically EC-like, and EC4 as most mesenchymal with minimal effects elicited by siERG and IL1B. Lastly, accessible chromatin regions unique to EC2 and EC4 were most enriched for coronary artery disease (CAD)-associated single-nucleotide polymorphisms from Genome Wide Association Studies (GWAS), suggesting that these cell phenotypes harbor CAD-modulating mechanisms. Primary EC cultures contain markedly heterogeneous cell subtypes defined by their molecular profiles. Surprisingly, the perturbations used here only modestly shifted cells between subpopulations, suggesting relatively stable molecular phenotypes in culture. Identifying consistently heterogeneous EC subpopulations between in vitro and ex vivo models should pave the way for improving in vitro systems while enabling the mechanisms governing heterogeneous cell state decisions.
Keywords: ERG; atherosclerosis; chromosomes; endothelial cells; epigenetics; gene expression; genetics; genomics; human; inflammation; vascular biology.
© 2023, Adelus et al.
Conflict of interest statement
MA, JD, BT, AC, AG, LS, MW, DC, CR No competing interests declared
Figures



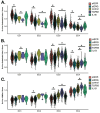
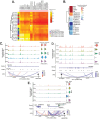

Update of
-
Single cell 'omic profiles of human aortic endothelial cells in vitro and human atherosclerotic lesions ex vivo reveals heterogeneity of endothelial subtype and response to activating perturbations.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 17:2023.04.03.535495. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.03.535495. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2024 Apr 05;12:RP91729. doi: 10.7554/eLife.91729. PMID: 37066416 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Aragam KG, Jiang T, Goel A, Kanoni S, Wolford BN, Atri DS, Weeks EM, Wang M, Hindy G, Zhou W, Grace C, Roselli C, Marston NA, Kamanu FK, Surakka I, Venegas LM, Sherliker P, Koyama S, Ishigaki K, Åsvold BO, Brown MR, Brumpton B, de Vries PS, Giannakopoulou O, Giardoglou P, Gudbjartsson DF, Güldener U, Haider SMI, Helgadottir A, Ibrahim M, Kastrati A, Kessler T, Kyriakou T, Konopka T, Li L, Ma L, Meitinger T, Mucha S, Munz M, Murgia F, Nielsen JB, Nöthen MM, Pang S, Reinberger T, Schnitzler G, Smedley D, Thorleifsson G, von Scheidt M, Ulirsch JC, Biobank Japan. EPIC-CVD. Arnar DO, Burtt NP, Costanzo MC, Flannick J, Ito K, Jang D-K, Kamatani Y, Khera AV, Komuro I, Kullo IJ, Lotta LA, Nelson CP, Roberts R, Thorgeirsson G, Thorsteinsdottir U, Webb TR, Baras A, Björkegren JLM, Boerwinkle E, Dedoussis G, Holm H, Hveem K, Melander O, Morrison AC, Orho-Melander M, Rallidis LS, Ruusalepp A, Sabatine MS, Stefansson K, Zalloua P, Ellinor PT, Farrall M, Danesh J, Ruff CT, Finucane HK, Hopewell JC, Clarke R, Gupta RM, Erdmann J, Samani NJ, Schunkert H, Watkins H, Willer CJ, Deloukas P, Kathiresan S, Butterworth AS, CARDIoGRAMplusC4D Consortium Discovery and systematic characterization of risk variants and genes for coronary artery disease in over a million participants. Nature Genetics. 2022;54:1803–1815. doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01233-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. 1995;57:289–300. doi: 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

