Neural assemblies coordinated by cortical waves are associated with waking and hallucinatory brain states
- PMID: 38578827
- PMCID: PMC12455724
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114017
Neural assemblies coordinated by cortical waves are associated with waking and hallucinatory brain states
Abstract
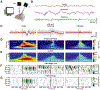
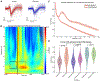
The relationship between sensory stimuli and perceptions is brain-state dependent: in wakefulness, suprathreshold stimuli evoke perceptions; under anesthesia, perceptions are abolished; and during dreaming and in dissociated states, percepts are internally generated. Here, we exploit this state dependence to identify brain activity associated with internally generated or stimulus-evoked perceptions. In awake mice, visual stimuli phase reset spontaneous cortical waves to elicit 3-6 Hz feedback traveling waves. These stimulus-evoked waves traverse the cortex and entrain visual and parietal neurons. Under anesthesia as well as during ketamine-induced dissociation, visual stimuli do not disrupt spontaneous waves. Uniquely, in the dissociated state, spontaneous waves traverse the cortex caudally and entrain visual and parietal neurons, akin to stimulus-evoked waves in wakefulness. Thus, coordinated neuronal assemblies orchestrated by traveling cortical waves emerge in states in which perception can manifest. The awake state is privileged in that this coordination is reliably elicited by external visual stimuli.
Keywords: CP: Neuroscience; VEP; anesthesia; feedback; hallucination; isoflurane; ketamine; state specific; traveling waves; travelling cortical waves; visual evoked potential.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
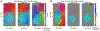
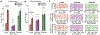
Update of
-
Neural assemblies coordinated by cortical waves are associated with waking and hallucinatory brain states.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 23:2023.05.22.540656. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.22.540656. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cell Rep. 2024 Apr 23;43(4):114017. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114017. PMID: 37292587 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Singer W. (2011). Consciousness and neuronal synchronization. Neurol. Conscious, 43–52.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

