Exploring the mechanism of ShenGui capsule in treating heart failure based on network pharmacology and molecular docking: A review
- PMID: 38579077
- PMCID: PMC10994518
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037512
Exploring the mechanism of ShenGui capsule in treating heart failure based on network pharmacology and molecular docking: A review
Abstract
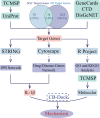
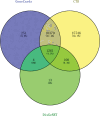
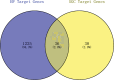
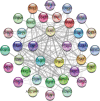
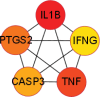
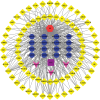
ShenGui capsule (SGC), as a herbal compound, has significant effects on the treatment of heart failure (HF), but its mechanism of action is unclear. In this study, we aimed to explore the potential pharmacological targets and mechanisms of SGC in the treatment of HF using network pharmacology and molecular docking approaches. Potential active ingredients of SGC were obtained from the traditional Chinese medicine systems pharmacology database and analysis platform database and screened by pharmacokinetic parameters. Target genes of HF were identified by comparing the toxicogenomics database, GeneCards, and DisGeNET databases. Protein interaction networks and gene-disorder-target networks were constructed using Cytoscape for visual analysis. Gene ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes were also performed to identify protein functional annotations and potential target signaling pathways through the DAVID database. CB-DOCK was used for molecular docking to explore the role of IL-1β with SGC compounds. Sixteen active ingredients in SGC were screened from the traditional Chinese medicine systems pharmacology database and analysis platform, of which 36 target genes intersected with HF target genes. Protein-protein interactions suggested that each target gene was closely related, and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) was identified as Hub gene. The network pharmacology analysis suggested that these active ingredients were well correlated with HF. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment analysis suggested that target genes were highly enriched in pathways such as inflammation. Molecular docking results showed that IL-1β binds tightly to SGC active components. This experiment provides an important research basis for the mechanism of action of SGC in the treatment of HF. In this study, the active compounds of SGC were found to bind IL-1β for the treatment of heart failure.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

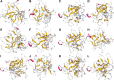
References
-
- McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, et al. ESC Scientific Document Group. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2021;42:3599–726. - PubMed
-
- Tsao CW, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2022 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2022;145:e153–639. - PubMed
-
- Braunwald E. Heart failure. JACC Heart Fail. 2013;1:1–20. - PubMed
-
- Murphy SP, Kakkar R, McCarthy CP, et al. Inflammation in heart failure: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:1324–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

