ALYREF m5C RNA methylation reader predicts bladder cancer prognosis by regulating the tumor immune microenvironment
- PMID: 38579085
- PMCID: PMC10994465
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037590
ALYREF m5C RNA methylation reader predicts bladder cancer prognosis by regulating the tumor immune microenvironment
Abstract
Background: 5-Methylcytidine (m5C) methylation is a recently emerging epigenetic modification that is closely related to tumor proliferation, occurrence, and metastasis. This study aimed to investigate the clinicopathological characteristics and prognostic value of m5C regulators in bladder cancer (BLCA), and their correlation with the tumor immune microenvironment.
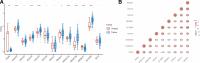
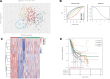
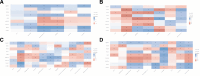
Methods: Thirteen m5C RNA methylation regulators were analyzed using RNA-sequencing and corresponding clinical information obtained from the TCGA database. The Cluster Profiler package was used to analyze the gene ontology function of potential targets and enriched the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was used to compare survival differences using the log-rank test and univariate Cox proportional hazards regression. The correlation between signature prognostic m5C regulators and various immune cells was analyzed. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses identified independence of the ALYREF gene signature.
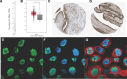
Results: Nine out of the 13 m5C RNA methylation regulators were differentially expressed in BLCA and normal samples and were co-expressed. These 9 regulators were associated with clinicopathological tumor characteristics, particularly high or low tumor risk, pT or pTNM stage, and migration. Consensus clustering analysis divides the BLCA samples into 4 clusters. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment annotation and gene ontology function analysis identified 273 upregulated and 594 downregulated genes in BLCA. Notably, only ALYREF was significantly correlated with OS (P < .05). ALYREF exhibited significant infiltration levels in macrophage cells. Therefore, we constructed a nomogram for ALYREF as an independent prognostic factor. Additionally, we observed that both the mRNA and protein levels of ALYREF were upregulated, and immunofluorescence showed that ALYREF was mainly distributed in nuclear speckles. ALYREF overexpression was significantly associated with poor OS.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrated the potential of ALYREF to predict clinical prognostic risks in BLCA patients and regulate the tumor immune microenvironment. As such, ALYREF may serve as a novel prognostic indicator in BLCA patients.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures





References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Rose TL, Milowsky MI. Improving systemic chemotherapy for bladder cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. 2016;18:27. - PubMed
-
- Craig AJ, von Felden J, Garcia-Lezana T, et al. Tumour evolution in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;17:139–52. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

