MLL4 binds TET3
- PMID: 38579707
- PMCID: PMC11162309
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2024.03.005
MLL4 binds TET3
Abstract
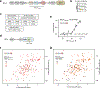
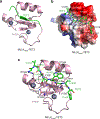
Human mixed lineage leukemia 4 (MLL4), also known as KMT2D, regulates cell type specific transcriptional programs through enhancer activation. Along with the catalytic methyltransferase domain, MLL4 contains seven less characterized plant homeodomain (PHD) fingers. Here, we report that the sixth PHD finger of MLL4 (MLL4PHD6) binds to the hydrophobic motif of ten-eleven translocation 3 (TET3), a dioxygenase that converts methylated cytosine into oxidized derivatives. The solution NMR structure of the TET3-MLL4PHD6 complex and binding assays show that, like histone H4 tail, TET3 occupies the hydrophobic site of MLL4PHD6, and that this interaction is conserved in the seventh PHD finger of homologous MLL3 (MLL3PHD7). Analysis of genomic localization of endogenous MLL4 and ectopically expressed TET3 in mouse embryonic stem cells reveals a high degree overlap on active enhancers and suggests a potential functional relationship of MLL4 and TET3.
Keywords: MLL4; PHD finger; TET3; interaction; structure.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Schindler U, Beckmann H, Cashmore AR, and Schindler TF (1993). HAT3.1, a novel Arabidopsis homeodomain protein containing a conserved cysteine-rich region. Plant Journal 4, 137–150. - PubMed
-
- Wysocka J, Swigut T, Xiao H, Milne TA, Kwon SY, Landry J, Kauer M, Tackett AJ, Chait BT, Badenhorst P, et al. (2006). A PHD finger of NURF couples histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation with chromatin remodelling. Nature 442, 86–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

