GABA system as the cause and effect in early development
- PMID: 38579901
- PMCID: PMC11081854
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2024.105651
GABA system as the cause and effect in early development
Abstract
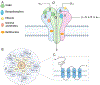
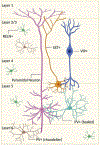
GABA is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the adult brain and through its actions on GABAARs, it protects against excitotoxicity and seizure activity, ensures temporal fidelity of neurotransmission, and regulates concerted rhythmic activity of neuronal populations. In the developing brain, the development of GABAergic neurons precedes that of glutamatergic neurons and the GABA system serves as a guide and framework for the development of other brain systems. Despite this early start, the maturation of the GABA system also continues well into the early postnatal period. In this review, we organize evidence around two scenarios based on the essential and protracted nature of GABA system development: 1) disruptions in the development of the GABA system can lead to large scale disruptions in other developmental processes (i.e., GABA as the cause), 2) protracted maturation of this system makes it vulnerable to the effects of developmental insults (i.e., GABA as the effect). While ample evidence supports the importance of GABA/GABAAR system in both scenarios, large gaps in existing knowledge prevent strong mechanistic conclusions.
Keywords: Early development; Early life stress; Fetal alcohol syndrome; GABA; GABAA receptors; Maternal immune activation.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest None
Figures

References
-
- Antonov SA, Novosadova EV, Arsenyeva EL, Grefenstein MA, Zykova AA, Kobylyansky AG, Manuilova ES, Grivennikov IA, Illarioshkin SN, & Myasoedov NF (2016, Sep). Investigation of the effects of GABA receptor agonists in the differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into dopaminergic neurons. Dokl Biol Sci, 470(1), 244–246. 10.1134/S0012496616050045 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Awad PN, Amegandjin CA, Szczurkowska J, Carrico JN, Fernandes do Nascimento AS, Baho E, Chattopadhyaya B, Cancedda L, Carmant L, & Di Cristo G (2018, Nov 1). KCC2 Regulates Dendritic Spine Formation in a Brain-Region Specific and BDNF Dependent Manner. Cereb Cortex, 28(11), 4049–4062. 10.1093/cercor/bhy198 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

