The One Hour Human Proteome
- PMID: 38579929
- PMCID: PMC11103439
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2024.100760
The One Hour Human Proteome
Abstract
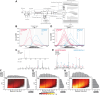
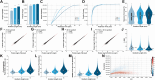
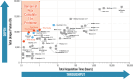
We describe deep analysis of the human proteome in less than 1 h. We achieve this expedited proteome characterization by leveraging state-of-the-art sample preparation, chromatographic separations, and data analysis tools, and by using the new Orbitrap Astral mass spectrometer equipped with a quadrupole mass filter, a high-field Orbitrap mass analyzer, and an asymmetric track lossless (Astral) mass analyzer. The system offers high tandem mass spectrometry acquisition speed of 200 Hz and detects hundreds of peptide sequences per second within data-independent acquisition or data-dependent acquisition modes of operation. The fast-switching capabilities of the new quadrupole complement the sensitivity and fast ion scanning of the Astral analyzer to enable narrow-bin data-independent analysis methods. Over a 30-min active chromatographic method consuming a total analysis time of 56 min, the Q-Orbitrap-Astral hybrid MS collects an average of 4319 MS1 scans and 438,062 tandem mass spectrometry scans per run, producing 235,916 peptide sequences (1% false discovery rate). On average, each 30-min analysis achieved detection of 10,411 protein groups (1% false discovery rate). We conclude, with these results and alongside other recent reports, that the 1-h human proteome is within reach.
Keywords: CRISPR; data independent acquisition; high throughput; instrumentation; mass spectrometry; proteome; proteomics; single shot; technology development.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): J. J. C. is a consultant for Thermo Fisher Scientific, Seer, and 908 Devices. T. N. A., E. D., A. P., M. Z., D. H., H. S., C. H., A. M., and V. Z. are employees of Thermo Fisher Scientific.
Figures



References
-
- Liu Y., Beyer A., Aebersold R. On the dependency of cellular protein levels on mRNA abundance. Cell. 2016;165:535–550. - PubMed
-
- Aebersold R., Mann M. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature. 2003;422:198–207. - PubMed
-
- Yates J.R., Ruse C.I., Nakorchevsky A. Proteomics by mass spectrometry: approaches, advances, and applications. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2009;11:49–79. - PubMed

