Rate control or revascularisation in managing atrial fibrillation-induced myocardial infarction and heart failure?
- PMID: 38580210
- PMCID: PMC11087898
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinme.2024.100034
Rate control or revascularisation in managing atrial fibrillation-induced myocardial infarction and heart failure?
Abstract
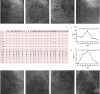
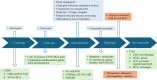
Acute myocardial infarction (MI) is a common and severe cardiovascular emergency that requires immediate treatment. Angina pectoris, which typically signals myocardial ischaemia, can appear in MI cases with myriad causes aside from coronary artery disease. However, not all MI patients benefit from invasive revascularisation therapy. We herein report a case involving a 78-year-old female patient with a complex medical history, including non-ST-segment elevation MI and coronary artery bypass grafting, who experienced recurrent chest pain. Instead of a direct result of coronary artery disease, her chest pain was later found to be primarily induced by atrial fibrillation (AF). Consequently, we shifted the focus of management to effective rate control for the AF after careful evaluation and achieved a satisfactory result. This case highlights the successful identification and timely application of intensive heart rate control management in an MI case induced by AF.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Heart failure; Myocardial infarction; Rate control.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018) Circulation. 2018;138:e618–e651. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

