Heterogeneous associations between interleukin-6 receptor variants and phenotypes across ancestries and implications for therapy
- PMID: 38580710
- PMCID: PMC10997791
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-54063-3
Heterogeneous associations between interleukin-6 receptor variants and phenotypes across ancestries and implications for therapy
Abstract
The Phenome-Wide Association Study (PheWAS) is increasingly used to broadly screen for potential treatment effects, e.g., IL6R variant as a proxy for IL6R antagonists. This approach offers an opportunity to address the limited power in clinical trials to study differential treatment effects across patient subgroups. However, limited methods exist to efficiently test for differences across subgroups in the thousands of multiple comparisons generated as part of a PheWAS. In this study, we developed an approach that maximizes the power to test for heterogeneous genotype-phenotype associations and applied this approach to an IL6R PheWAS among individuals of African (AFR) and European (EUR) ancestries. We identified 29 traits with differences in IL6R variant-phenotype associations, including a lower risk of type 2 diabetes in AFR (OR 0.96) vs EUR (OR 1.0, p-value for heterogeneity = 8.5 × 10-3), and higher white blood cell count (p-value for heterogeneity = 8.5 × 10-131). These data suggest a more salutary effect of IL6R blockade for T2D among individuals of AFR vs EUR ancestry and provide data to inform ongoing clinical trials targeting IL6 for an expanding number of conditions. Moreover, the method to test for heterogeneity of associations can be applied broadly to other large-scale genotype-phenotype screens in diverse populations.
© 2024. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
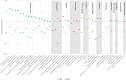
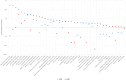


References
-
- Gaziano JM, Concato J, Brophy M, Fiore L, Pyarajan S, Breeling J, Whitbourne S, Deen J, Shannon C, Humphries D, Guarino P. Million Veteran Program: A mega-biobank to study genetic influences on health and disease. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2016;70:214–223. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2015.09.016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Finan C, Gaulton A, Kruger FA, Lumbers RT, Shah T, Engmann J, Galver L, Kelley R, Karlsson A, Santos R, Overington JP. The druggable genome and support for target identification and validation in drug development. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017;9(383):eaag1166. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aag1166. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ferreira RC, Freitag DF, Cutler AJ, Howson JM, Rainbow DB, Smyth DJ, Kaptoge S, Clarke P, Boreham C, Coulson RM, Pekalski ML. Functional IL6R 358Ala allele impairs classical IL-6 receptor signaling and influences risk of diverse inflammatory diseases. PLoS Genet. 2013;9(4):e1003444. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003444. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cai T, Zhang Y, Ho YL, Link N, Sun J, Huang J, Cai TA, Damrauer S, Ahuja Y, Honerlaw J, Costa L. Association of interleukin 6 receptor variant with cardiovascular disease effects of interleukin 6 receptor blocking therapy: A phenome-wide association study. JAMA Cardiol. 2018;3(9):849–857. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2018.2287. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

