Effect of a nutraceutical combination on sleep quality among people with impaired sleep: a randomised, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 38580720
- PMCID: PMC10997602
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-58661-z
Effect of a nutraceutical combination on sleep quality among people with impaired sleep: a randomised, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
In this randomised, placebo-controlled trial, adults with impaired sleep (Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index ≥ 5) were randomly assigned using a minimization algorithm to receive a formulation containing L-theanine plus lemon balm, valerian, and saffron extracts, or placebo, during 6 weeks. Objective sleep quality parameters were measured using an actigraphy device. We enrolled and randomised 64 individuals, 31 from the active group and 27 from the placebo group completed the 6 week follow-up. Mean sleep efficiency remained unmodified in the active group, and increased by 3% in the placebo group, the between-group difference in the change was not statistically significant (p = 0.49). Total sleep time also improved more with placebo (13.0 vs. 1.33 min, p = 0.66). Time wake after sleep onset (WASO) decreased more in the active group (4.6% vs. 2.4%), but the difference was not significant (p = 0.33). Mean PSQI decreased by 3.11 points (32.3%) in the active group, and by 3.86 points (39.5%) in the placebo group (p = 0.41). SF-36 increased more with placebo (+ 18.3 in active, + 32.1 in placebo, p = 0.68). Salivary cortisol remained unchanged in both groups. No serious adverse events were reported. Among adults with impaired sleep, a nutraceutical combination did not improve objective or subjective sleep parameters more than a placebo infusion.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
This study was funded by Team Foods Colombia, but the sponsor was not involved in the study conduct or analysis, or in the decision to publish.
Figures

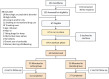
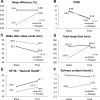
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

