Regulation of cargo selection in exosome biogenesis and its biomedical applications in cancer
- PMID: 38580812
- PMCID: PMC11059157
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-024-01209-y
Regulation of cargo selection in exosome biogenesis and its biomedical applications in cancer
Abstract
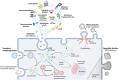
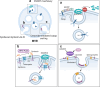
Extracellular vesicles (EVs), including exosomes, are increasingly recognized as potent mediators of intercellular communication due to their capacity to transport a diverse array of bioactive molecules. They assume vital roles in a wide range of physiological and pathological processes and hold significant promise as emerging disease biomarkers, therapeutic agents, and carriers for drug delivery. Exosomes encompass specific groups of membrane proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, cytosolic proteins, and other signaling molecules within their interior. These cargo molecules dictate targeting specificity and functional roles upon reaching recipient cells. Despite our growing understanding of the significance of exosomes in diverse biological processes, the molecular mechanisms governing the selective sorting and packaging of cargo within exosomes have not been fully elucidated. In this review, we summarize current insights into the molecular mechanisms that regulate the sorting of various molecules into exosomes, the resulting biological functions, and potential clinical applications, with a particular emphasis on their relevance in cancer and other diseases. A comprehensive understanding of the loading processes and mechanisms involved in exosome cargo sorting is essential for uncovering the physiological and pathological roles of exosomes, identifying therapeutic targets, and advancing the clinical development of exosome-based therapeutics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Harding C, Heuser J, Stahl P. Endocytosis and intracellular processing of transferrin and colloidal gold-transferrin in rat reticulocytes: demonstration of a pathway for receptor shedding. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1984;35:256–263. - PubMed
-
- Shurtleff MJ, Temoche-Diaz MM, Schekman R. Extracellular vesicles and cancer: caveat lector. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2018;2:395–411. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-030617-050519. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

