Comorbidities in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a sibling study
- PMID: 38580996
- PMCID: PMC10996169
- DOI: 10.1186/s12905-024-03028-9
Comorbidities in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a sibling study
Abstract
Background: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) has previously been associated with several comorbidities that may have shared genetic, epigenetic, developmental or environmental origins. PCOS may be influenced by prenatal androgen excess, poor intrauterine or childhood environmental factors, childhood obesity and learned health risk behaviors. We analyzed the association between PCOS and several relevant comorbidities while adjusting for early-life biological and socioeconomic conditions, also investigating the extent to which the association is affected by familial risk factors.
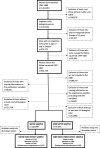
Methods: This total-population register-based cohort study included 333,999 full sisters, born between 1962 and 1980. PCOS and comorbidity diagnoses were measured at age 17-45 years through national hospital register data from 1997 to 2011, and complemented with information on the study subjects´ early-life and social characteristics. In the main analysis, sister fixed effects (FE) models were used to control for all time-invariant factors that are shared among sisters, thereby testing whether the association between PCOS and examined comorbidities is influenced by unobserved familial environmental, social or genetic factors.
Results: Three thousand five hundred seventy women in the Sister sample were diagnosed with PCOS, of whom 14% had obesity, 8% had depression, 7% had anxiety and 4% experienced sleeping, sexual and eating disorders (SSE). Having PCOS increased the odds of obesity nearly 6-fold (adjusted OR (aOR): 5.9 [95% CI:5.4-6.5]). This association was attenuated in models accounting for unobserved characteristics shared between full sisters, but remained considerable in size (Sister FE: aOR: 4.5 [95% CI: 3.6-5.6]). For depression (Sister FE: aOR: 1.4 [95% CI: 1.2-1.8]) and anxiety (Sister FE: aOR: 1.5 [95% CI: 1.2-1.8), there was a small decrease in the aORs when controlling for factors shared between sisters. Being diagnosed with SSE disorders yielded a 2.4 aOR (95% CI:2.0-2.6) when controlling for a comprehensive set of individual-level confounders, which only decreased slightly when controlling for factors at the family level such as shared genes or parenting style. Accounting for differences between sisters in observed early-life circumstances influenced the estimated associations marginally.
Conclusion: Having been diagnosed with PCOS is associated with a markedly increased risk of obesity and sleeping, sexual and eating disorders, also after accounting for factors shared between sisters and early-life conditions.
Keywords: Comorbidity; Polycystic ovary syndrome; Sibling fixed effect.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157:107843. 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical