Anxiety and depression status in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and outcomes of nintedanib treatment: an observational study
- PMID: 38581666
- PMCID: PMC11000612
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2323097
Anxiety and depression status in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and outcomes of nintedanib treatment: an observational study
Abstract
Background: Anxiety and depression are common comorbidities in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) that impair health-related quality of life. However, there is a lack of studies focusing on the mental disorder of IPF after antifibrotic treatment and their related predictive factors.
Methods: Patients with an initial diagnosis of IPF were enrolled. Data on demographics, lung function, Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7) Scale, Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9), Patient Health Questionnaire-15 (PHQ-15), and St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire total score(SGRQ-T) were collected. Changes in anxiety, depression, somatic symptoms, and quality of life scores before and after nintedanib treatment were compared, and the related predictive factors were analyzed.
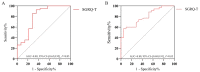
Results: A total of 56 patients with a first diagnosis of IPF were enrolled, with 42 and 35 patients suffering from anxiety and depression, respectively. The GAD-7, PHQ-9, PHQ-15, and SGRQ scores were higher in the anxiety and depression groups. SGRQ total score (SGRQ-T) [OR = 1.075, 95%CI= (1.011, 1.142)] was an independent predictor of IPF combined with anxiety (p < 0.05); SGRQ-T [OR = 1.080, 95%CI= (1.001, 1.167)] was also an independent predictor of IPF combined with depression (p < 0.05). After treatment, GAD-7, PHQ-9, PHQ-15, and SGRQ scores decreased (p < 0.05). ΔSGRQ-T significantly affected ΔGAD-7 (β = 0.376, p = 0.009) and ΔPHQ-9 (β = 0.329, p = 0.022).
Conclusion: Anxiety and depression in IPF patients are closely related to somatic symptoms, pulmonary function, and quality of life. The SGRQ-T score is of great value for assessing anxiety and depression in patients with IPF. Short-term treatment with nintedanib antifibrotic therapy can alleviate anxiety and depression in IPF patients.
Keywords: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; antifibrotic therapy; anxiety; depression; quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Quality of life in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in Latin American countries.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 Jan 24;25(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03506-2. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 39856586 Free PMC article.
-
Health-related quality of life and symptoms in patients with IPF treated with nintedanib: analyses of patient-reported outcomes from the INPULSIS® trials.Respir Res. 2020 Jan 30;21(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-1298-1. Respir Res. 2020. PMID: 32000772 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The impact of palliative care on quality of life, anxiety, and depression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a randomized controlled pilot study.Respir Res. 2020 Jan 3;21(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1266-9. Respir Res. 2020. PMID: 31900187 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The psychometric properties of the St George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a literature review.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014 Aug 20;12:124. doi: 10.1186/s12955-014-0124-1. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014. PMID: 25138056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of antifibrotic drugs, nintedanib and pirfenidone, in treatment of progressive pulmonary fibrosis in both idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and non-IPF: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Pulm Med. 2021 Dec 11;21(1):411. doi: 10.1186/s12890-021-01783-1. BMC Pulm Med. 2021. PMID: 34895203 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exercise improves pulmonary fibrosis and neurological symptoms via S100A12 inhibition.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 27;16:1583827. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1583827. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40655156 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressant intervention to possibly delay disease progression and frailty in elderly idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients: a clinical trial.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2025 Mar 22;37(1):101. doi: 10.1007/s40520-025-03009-4. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2025. PMID: 40120048 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Chronic Lung Diseases and Depressive Symptoms in Older Adults: Insights from Observational Studies and Mendelian Randomization.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2025 Jun 15;18:3465-3475. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S515745. eCollection 2025. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2025. PMID: 40538380 Free PMC article.
-
Mental health burden in progressive pulmonary fibrosis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Depression and anxiety.Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2025 Jun 25;42(2):16342. doi: 10.36141/svdld.v42i2.16342. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2025. PMID: 40699499 Free PMC article.
-
Perception of Gratitude During an Online Mindfulness-Based Intervention (eMBI) in Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease in Brazil: An Exploratory Qualitative Study.J Relig Health. 2024 Nov 18. doi: 10.1007/s10943-024-02177-3. Online ahead of print. J Relig Health. 2024. PMID: 39551832
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
