Functionally diverse thymic medullary epithelial cells interplay to direct central tolerance
- PMID: 38581680
- PMCID: PMC11079940
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114072
Functionally diverse thymic medullary epithelial cells interplay to direct central tolerance
Abstract
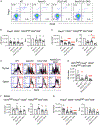
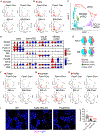
Medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTECs) are essential for the establishment of self-tolerance in T cells. Promiscuous gene expression by a subpopulation of mTECs regulated by the nuclear protein Aire contributes to the display of self-genomic products to newly generated T cells. Recent reports have highlighted additional self-antigen-displaying mTEC subpopulations, namely Fezf2-expressing mTECs and a mosaic of self-mimetic mTECs including thymic tuft cells. In addition, a functionally different subset of mTECs produces chemokine CCL21, which attracts developing thymocytes to the medullary region. Here, we report that CCL21+ mTECs and Aire+ mTECs non-redundantly cooperate to direct self-tolerance to prevent autoimmune pathology by optimizing the deletion of self-reactive T cells and the generation of regulatory T cells. We also detect cooperation for self-tolerance between Aire and Fezf2, the latter of which unexpectedly regulates thymic tuft cells. Our results indicate an indispensable interplay among functionally diverse mTECs for the establishment of central self-tolerance.
Keywords: Aire; CCL21; CP: Immunology; Fezf2; autoimmunity; central tolerance; medullary thymic epithelial cell; negative selection; regulatory T cell; thymic tuft cell; thymus medulla.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
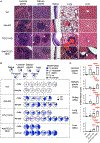
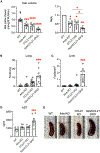
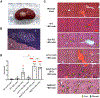
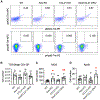

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

