Synergizing biotechnology and natural farming: pioneering agricultural sustainability through innovative interventions
- PMID: 38584951
- PMCID: PMC10995308
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1280846
Synergizing biotechnology and natural farming: pioneering agricultural sustainability through innovative interventions
Abstract
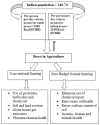
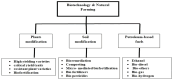
The world has undergone a remarkable transformation from the era of famines to an age of global food production that caters to an exponentially growing population. This transformation has been made possible by significant agricultural revolutions, marked by the intensification of agriculture through the infusion of mechanical, industrial, and economic inputs. However, this rapid advancement in agriculture has also brought about the proliferation of agricultural inputs such as pesticides, fertilizers, and irrigation, which have given rise to long-term environmental crises. Over the past two decades, we have witnessed a concerning plateau in crop production, the loss of arable land, and dramatic shifts in climatic conditions. These challenges have underscored the urgent need to protect our global commons, particularly the environment, through a participatory approach that involves countries worldwide, regardless of their developmental status. To achieve the goal of sustainability in agriculture, it is imperative to adopt multidisciplinary approaches that integrate fields such as biology, engineering, chemistry, economics, and community development. One noteworthy initiative in this regard is Zero Budget Natural Farming, which highlights the significance of leveraging the synergistic effects of both plant and animal products to enhance crop establishment, build soil fertility, and promote the proliferation of beneficial microorganisms. The ultimate aim is to create self-sustainable agro-ecosystems. This review advocates for the incorporation of biotechnological tools in natural farming to expedite the dynamism of such systems in an eco-friendly manner. By harnessing the power of biotechnology, we can increase the productivity of agro-ecology and generate abundant supplies of food, feed, fiber, and nutraceuticals to meet the needs of our ever-expanding global population.
Keywords: bio-fortification; bio-fuels; biotechnology; natural farming; resistance.
Copyright © 2024 Badiyal, Mahajan, Rana, Sood, Walia, Rana, Manhas and Jayswal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abbey L., Abbey J., Leke-Aladekoba A., Iheshiulo E. M. A., Ijenyo M. (2019). “Biopesticides and biofertilizers: types, production, benefits, and utilization,” in Byproducts from agriculture and fisheries: adding value for food, feed, pharma, and fuels, 479–500.
-
- ABLE INDIA . (2013). Biospectrum ABLE industry survey. Available online at: http://www.ableIndia.in/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/11th-able-biospectrum....
-
- Ahangar M. A., Wani S. H., Dar Z. A., Roohi J., Mohiddin F., Bansal M., et al. . (2022). Distribution, etiology, molecular genetics and management perspectives of northern corn leaf blight of maize (Zea mays L.). Phyton 91 (10), 1–23. (0031-9457).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous