Next Generation Sequencing in orthopaedic infections - Where is the road headed?
- PMID: 38585384
- PMCID: PMC10998229
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcot.2024.102397
Next Generation Sequencing in orthopaedic infections - Where is the road headed?
Abstract
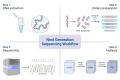
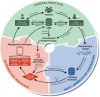
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has emerged as a game changer in the field of orthopaedic diagnostics, notably in the detection and management of infections associated with prosthetic joints and implants. This paper conducts an exhaustive examination of the pivotal role, outcomes, and prospective future uses of NGS in diagnosing orthopaedic infections. In comparison to conventional culture-based methods, NGS offers a marked improvement in sensitivity thereby facilitating prompt and comprehensive identification of pathogens. This encompasses the ability to detect polymicrobial infections, antibiotic-resistant strains, and previously imperceptible microorganisms. Furthermore, this article delves into the technology's contribution to advancing personalized medicine and promoting judicious antibiotic use. Nonetheless, the seamless integration of NGS into routine clinical practice is impeded by challenges such as substantial financial outlays, the requisite for specialized equipment and expertise, and the intricacy associated with data analysis. Notwithstanding these impediments, the potential for NGS to revolutionize orthopaedic diagnostics remains substantial, with ongoing advancements poised to address current limitations and broaden its scope within clinical applications.
Keywords: Antibiotic resistance; Bioinformatics; Molecular diagnostics; Next generation sequencing; Orthopaedic infections; Prosthetic joint infections.
© 2024 Delhi Orthopedic Association. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have any competing interests in this article.The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictive Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing by Next-Generation Sequencing for Periprosthetic Joint Infections: Potential and Limitations.Biomedicines. 2021 Jul 29;9(8):910. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9080910. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34440114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Next-generation sequencing in cancer diagnosis and treatment: clinical applications and future directions.Discov Oncol. 2025 Apr 20;16(1):578. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-01816-9. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40253661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnosis and management of invasive fungal diseases by next-generation sequencing: are we there yet?Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2024 Dec 12:1-14. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2024.2436396. Online ahead of print. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2024. PMID: 39623670 Review.
-
Next-Generation Sequencing for Pathogen Identification in Infected Foot Ulcers.Foot Ankle Orthop. 2021 Jul 12;6(3):24730114211026933. doi: 10.1177/24730114211026933. eCollection 2021 Jul. Foot Ankle Orthop. 2021. PMID: 35097461 Free PMC article.
-
Utilizing Next-Generation Sequencing: Advancements in the Diagnosis of Fungal Infections.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Aug 1;14(15):1664. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14151664. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39125540 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Musculoskeletal infection, diagnosis and management.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2024 Dec 27;62:102898. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2024.102898. eCollection 2025 Mar. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2024. PMID: 39867591 No abstract available.
-
Management of periprosthetic joint infection of the shoulder: A narrative review.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2024 Aug 24;56:102520. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2024.102520. eCollection 2024 Sep. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2024. PMID: 39296861
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
