The Simultaneous Effects of miR-145-5p and hsa-let-7a-3p on Colorectal Tumorigenesis: In Vitro Evidence
- PMID: 38585468
- PMCID: PMC10997926
- DOI: 10.34172/apb.2024.004
The Simultaneous Effects of miR-145-5p and hsa-let-7a-3p on Colorectal Tumorigenesis: In Vitro Evidence
Abstract
Purpose: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a group of small regulatory non-coding RNAs, which are dysregulated through tumor progression. let-7 and MIR-145 are both tumor suppressor microRNAs that are downregulated in a wide array of cancers including colorectal cancer (CRC).
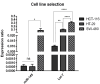
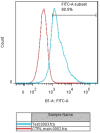
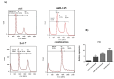
Methods: This study was aimed to investigate the effect of simultaneous replacement of these two tumor suppressor miRNAs on proliferation, apoptosis, and migration of CRC cells. HCT-116 with lower expression levels of hsa-let-7a-3p and MIR-145-5p was selected for functional investigations. The cells were cultured and transfected with hsa-let-7a and MIR-145, separately and in combination. Cell viability and apoptosis rates were assessed by MTT assay and flow cytometry, respectively. Cell cycle status was further evaluated using flow cytometry and qRT-PCR was employed to evaluate gene expression.
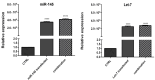
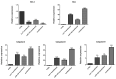
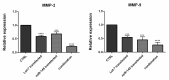
Results: The obtained results showed that exogenous overexpression of MIR-145 and hsa-let-7a in HCT-116 cells could cooperatively decrease CRC cell proliferation and induce sub-G1 cell cycle arrest. Moreover, hsa-let-7a and MIR-145 co-transfection significantly increased apoptosis induction compared to separate transfected cells and control through modulating the expression levels of apoptosis-related genes including Bax, Bcl-2, P53, Caspase-3, Caspase-8, and Caspase-9. Furthermore, qRT-PCR results illustrated that hsa-let-7a and MIR-145 combination more effectively downregulated MMP-9 and MMP-2 expression, as the important modulators of metastasis, compared to the controls.
Conclusion: Taken together, considering that exogenous overexpression of MIR-145 and hsa-let-7a showed cooperative anti-cancer effects on CRC cells, their combination may be considered as a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of CRC.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; MIR-145-5p; hsa-let-7a-3p.
©2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Positive regulation of innate immune response by miRNA-let-7a-5p.Front Genet. 2023 Jan 6;13:1025539. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1025539. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36685889 Free PMC article.
-
Let-7a-3p overexpression increases chemosensitivity to carmustine and synergistically promotes autophagy and suppresses cell survival in U87MG glioblastoma cancer cells.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Sep;397(9):6903-6918. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03060-4. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38587542
-
MTUS1 and its targeting miRNAs in colorectal carcinoma: significant associations.Tumour Biol. 2016 May;37(5):6637-45. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4550-4. Epub 2015 Dec 7. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26643896
-
Diagnostic Potential of NEAT1, hsa-let-7a-5p, and miR-506-3p in Early-stage Parkinson's Disease.Curr Med Chem. 2024 Oct 31. doi: 10.2174/0109298673336756241016063552. Online ahead of print. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39484776
-
Exploring the role of non-coding RNAs in atrial septal defect pathogenesis: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 22;19(8):e0306576. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306576. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39172906 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous effect of miR-21 suppression and miR-143 restoration on inhibition of proliferation and migration in SW-480 colorectal cancer cells.Bioimpacts. 2024 Jun 19;15:30255. doi: 10.34172/bi.30255. eCollection 2025. Bioimpacts. 2024. PMID: 39963562 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperatively inhibition effect of miR-143-5p and miR-145-5p in tumorigenesis of glioblastoma cells through modulating AKT signaling pathway.Bioimpacts. 2024;14(3):29913. doi: 10.34172/bi.2023.29913. Epub 2023 Nov 5. Bioimpacts. 2024. PMID: 38938754 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous