The Norwegian public's ability to assess treatment claims: results of a cross-sectional study of critical health literacy
- PMID: 38585673
- PMCID: PMC10995534
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.21902.2
The Norwegian public's ability to assess treatment claims: results of a cross-sectional study of critical health literacy
Abstract
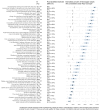
Background: Few studies have evaluated the ability of the general public to assess the trustworthiness of claims about the effects of healthcare. For the most part, those studies have used self-reported measures of critical health literacy. Methods: We mailed 4500 invitations to Norwegian adults. Respondents were randomly assigned to one of four online questionnaires that included multiple-choice questions that test understanding of Key Concepts people need to understand to assess healthcare claims. They also included questions about intended behaviours and self-efficacy. One of the four questionnaires was identical to one previously used in two randomised trials of educational interventions in Uganda, facilitating comparisons to Ugandan children, parents, and teachers. We adjusted the results using demographic data to reflect the population. Results: A total of 771 people responded. The adjusted proportion of Norwegian adults who answered correctly was < 50% for 17 of the 30 Key Concepts. On the other hand, less than half answered correctly for 13 concepts. The results for Norwegian adults were better than the results for Ugandan children in the intervention arm of the trial and parents, and similar to those of Ugandan teachers in the intervention arm of the trial. Based on self-report, most Norwegians are likely to find out the basis of treatment claims, but few consider it easy to assess whether claims are based on research and to assess the trustworthiness of research. Conclusions: Norwegian adults do not understand many concepts that are essential for assessing healthcare claims and making informed choices. Future interventions should be tailored to address Key Concepts for which there appears to be a lack of understanding.
Keywords: critical health literacy; critical thinking; evidence-based practice; evidence-informed decision-making; health literacy; public health; public understanding of science; shared decision making.
Copyright: © 2021 Dahlgren A et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: CJR has previously received income and research funding from, and has published with researchers employed by, biomedical sector companies including OncoImmunity (NEC), AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, and Genentech (Roche), and is named as inventor on patents and patent applications. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Chalmers I, Glasziou P, Badenoch D, et al. : Evidence Live 2016: Promoting informed healthcare choices by helping people assess treatment claims. BMJ. Reference Source
-
- Austvoll-Dahlgren A: Improving health literacy : identifying barriers and facilitators to people's ability to obtain health information, and the development and evaluation of an intervention to improve health literacy.Oslo: Unipub; 1 b. (flere pag.): ill. p.2012. Reference Source
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources