This is a preprint.
Integration of transcriptomics and long-read genomics prioritizes structural variants in rare disease
- PMID: 38585781
- PMCID: PMC10996727
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.03.22.24304565
Integration of transcriptomics and long-read genomics prioritizes structural variants in rare disease
Update in
-
Integration of transcriptomics and long-read genomics prioritizes structural variants in rare disease.Genome Res. 2025 Apr 14;35(4):914-928. doi: 10.1101/gr.279323.124. Genome Res. 2025. PMID: 40113264 Free PMC article.
Abstract
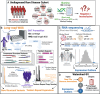
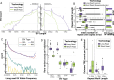
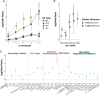
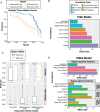
Rare structural variants (SVs) - insertions, deletions, and complex rearrangements - can cause Mendelian disease, yet they remain difficult to accurately detect and interpret. We sequenced and analyzed Oxford Nanopore long-read genomes of 68 individuals from the Undiagnosed Disease Network (UDN) with no previously identified diagnostic mutations from short-read sequencing. Using our optimized SV detection pipelines and 571 control long-read genomes, we detected 716 long-read rare (MAF < 0.01) SV alleles per genome on average, achieving a 2.4x increase from short-reads. To characterize the functional effects of rare SVs, we assessed their relationship with gene expression from blood or fibroblasts from the same individuals, and found that rare SVs overlapping enhancers were enriched (LOR = 0.46) near expression outliers. We also evaluated tandem repeat expansions (TREs) and found 14 rare TREs per genome; notably these TREs were also enriched near overexpression outliers. To prioritize candidate functional SVs, we developed Watershed-SV, a probabilistic model that integrates expression data with SV-specific genomic annotations, which significantly outperforms baseline models that don't incorporate expression data. Watershed-SV identified a median of eight high-confidence functional SVs per UDN genome. Notably, this included compound heterozygous deletions in FAM177A1 shared by two siblings, which were likely causal for a rare neurodevelopmental disorder. Our observations demonstrate the promise of integrating long-read sequencing with gene expression towards improving the prioritization of functional SVs and TREs in rare disease patients.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTEREST STATEMENT SBM is an advisor to BioMarin, Myome and Tenaya Therapeutics. AB is a co-founder of CellCipher, Inc, is a shareholder in Alphabet, Inc, and has consulted for Third Rock Ventures, LLC. EAA is the founder of Personalis, Deepcell, Svexa, RCD Co, Parameter Health, an advisor for SequenceBio, Foresite Labs, PacBio, a non-executive director at AstraZeneca, hold stocks in Oxford Nanopore, Pacific Biosciences, AstraZeneca, and offers collaborative support in kind to Illumina, Pacific Biosciences, Oxford Nanopore
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- U24 HG010263/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG048076/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HG013397/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG072573/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA272952/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 AG072290/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA253481/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG010218/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG011762/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG074339/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG012069/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG000044/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG066490/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM139580/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH125244/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS072248/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS134358/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD025082/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD034190/OD/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
