This is a preprint.
Wrapping of single-stranded DNA by Replication Protein A and modulation through phosphorylation
- PMID: 38585962
- PMCID: PMC10996701
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.03.28.587234
Wrapping of single-stranded DNA by Replication Protein A and modulation through phosphorylation
Update in
-
Partial wrapping of single-stranded DNA by replication protein A and modulation through phosphorylation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Oct 28;52(19):11626-11640. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae584. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38989614 Free PMC article.
Abstract
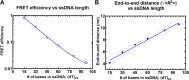
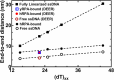
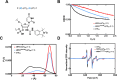
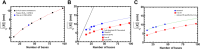
Single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) intermediates, which emerge during DNA metabolic processes are shielded by Replication Protein A (RPA). RPA binds to ssDNA and acts as a gatekeeper, directing the ssDNA towards downstream DNA metabolic pathways with exceptional specificity. Understanding the mechanistic basis for such RPA-dependent specificity requires a comprehensive understanding of the structural conformation of ssDNA when bound to RPA. Previous studies suggested a stretching of ssDNA by RPA. However, structural investigations uncovered a partial wrapping of ssDNA around RPA. Therefore, to reconcile the models, in this study, we measured the end-to-end distances of free ssDNA and RPA-ssDNA complexes using single-molecule FRET and Double Electron-Electron Resonance (DEER) spectroscopy and found only a small systematic increase in the end-to-end distance of ssDNA upon RPA binding. This change does not align with a linear stretching model but rather supports partial wrapping of ssDNA around the contour of DNA binding domains of RPA. Furthermore, we reveal how phosphorylation at the key Ser-384 site in the RPA70 subunit provides access to the wrapped ssDNA by remodeling the DNA-binding domains. These findings establish a precise structural model for RPA-bound ssDNA, providing valuable insights into how RPA facilitates the remodeling of ssDNA for subsequent downstream processes.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Wold M.S. (1997) Replication protein A: a heterotrimeric, single-stranded DNA-binding protein required for eukaryotic DNA metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem, 66, 61–92. - PubMed
-
- Iftode C., Daniely Y. and Borowiec J.A. (1999) Replication protein A (RPA): the eukaryotic SSB. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol, 34, 141–180. - PubMed
-
- Kim C., Paulus B.F. and Wold M.S. (1994) Interactions of human replication protein A with oligonucleotides. Biochemistry, 33, 14197–14206. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
