Screening of potential biomarkers in propofol-induced neurotoxicity via bioinformatics prediction and experimental verification
- PMID: 38586100
- PMCID: PMC10994811
- DOI: 10.62347/MTAY7931
Screening of potential biomarkers in propofol-induced neurotoxicity via bioinformatics prediction and experimental verification
Abstract
Objectives: To identify hub genes and biological processes of propofol-induced neurotoxicity and promote the development of pediatric anesthesiology.
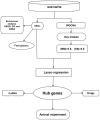
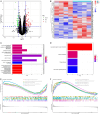
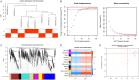
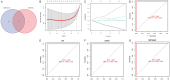
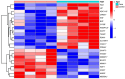
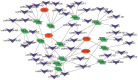
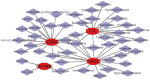
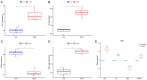
Methods: We downloaded the GSE106799 dataset from the Gene Expression Omnibus database. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were screened, then Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes, Gene Ontology and Gene Set Enrichment analyses were performed on all DEGs. We identified potential ferroptosis genes in the pathogenesis of propofol-induced neurotoxicity. A key module was obtained after performing weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) on the GSE106799 dataset. Hub genes were identified after the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression analysis of the intersection of DEGs and genes from the key module. We established a competing endogenous RNA network and predicted potential drugs according to the hub genes. Total RNA and proteins were extracted for real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting, respectively.
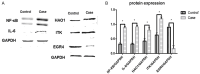
Results: A total of 112 DEGs, including 76 upregulated and 36 downregulated ones were screened out. Propofol-induced neurotoxicity involved processes such as nervous system development, activation of JAK/STAT and MAPK signaling pathways, vascular regeneration, and oxidative stress. The results of WGCNA suggested that the tan module was the most strongly associated with propofol-induced neurotoxicity. We identified 4 hub genes (EGR4, HAO1, ITK and GM14446) after LASSO regression analysis. Animal experiments demonstrated that propofol caused overexpression of the protein levels of HAO1, ITK and inflammatory factors in the brain, as well as the mRNA levels of HAO1, ITK and GM14446. Propofol inhibited expression of EGR4 at mRNA and protein levels.
Conclusions: Previous studies have demonstrated that EGR4, HAO1, ITK and GM14446 play a role in intellectual development, neuroinflammation and neuronal differentiation. These hub genes may help us to find new preventive and therapeutic targets for propofol-induced neurotoxicity.
Keywords: Propofol; neurotoxicity; potential biomarkers.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Six potential biomarkers in septic shock: a deep bioinformatics and prospective observational study.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 8;14:1184700. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1184700. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37359526 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of hub biomarkers and immune cell infiltration characteristics of polymyositis by bioinformatics analysis.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 26;13:1002500. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1002500. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36225941 Free PMC article.
-
The identification and verification of hub genes associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension using weighted gene co-expression network analysis.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Dec 13;22(1):474. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02275-6. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 36514015 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Effective Diagnostic Biomarkers and Immune Cell Infiltration in Atopic Dermatitis by Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jul 14;9:917077. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.917077. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35911963 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Hub Genes Associated With Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Robust Rank Aggregation Combined With Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis.Front Genet. 2020 Sep 30;11:895. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00895. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33133125 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lin EP, Soriano SG, Loepke AW. Anesthetic neurotoxicity. Anesthesiol Clin. 2014;32:133–155. - PubMed
-
- Bartkowska-Śniatkowska A, Rosada-Kurasińska J, Zielińska M, Bienert A. Do we really know the pharmacodynamics of anaesthetics used in newborns, infants and children? A review of the experimental and clinical data on neurodegeneration. Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther. 2014;46:101–108. - PubMed
-
- Liu F, Liu S, Patterson TA, Fogle C, Hanig JP, Wang C, Slikker W Jr. Protective effects of xenon on propofol-induced neurotoxicity in human neural stem cell-derived models. Mol Neurobiol. 2020;57:200–207. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
